Page 195 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd InOrganic Chemistry
P. 195
P1: GSS Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN009F-398 July 6, 2001 20:34
4 Main Group Elements
much simpler. However, the chemistry of boron is unique carboranes, and other derivatives of this remarkable el-
in that the bonding and structures of boron are built up ement offer myriad exciting and unusual examples.
in a fashion unparalleled even by carbon chemistry. The
complexities of the borides, borates, halides, boranes, A. Boron Carbide
Boron carbide is often represented as “B 4 C,” but this is
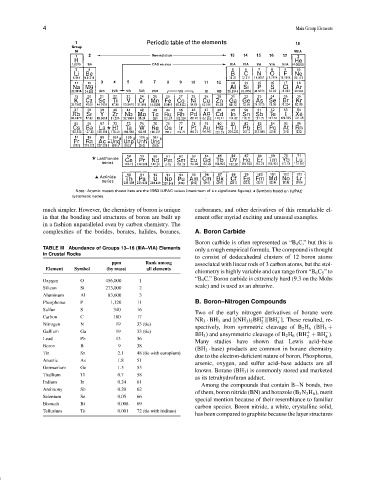
TABLE III Abundance of Groups 13–16 (IIIA–VIA) Elements only a rough empirical formula. The compound is thought
in Crustal Rocks
to consist of dodecahedral clusters of 12 boron atoms
ppm Rank among associated with linear rods of 3 carbon atoms, but the stoi-
Element Symbol (by mass) all elements
chiometry is highly variable and can range from “B 6 C 5 ” to
“B 4 C.” Boron carbide is extremely hard (9.3 on the Mohs
Oxygen O 456,000 1
scale) and is used as an abrasive.
Silicon Si 273,000 2
Aluminum Al 83,600 3
Phosphorus P 1,120 11 B. Boron–Nitrogen Compounds
Sulfur S 340 16
Two of the early nitrogen derivatives of borane were
Carbon C 180 17 + −
NR 3 · BH 3 and [(NH 3 ) 2 BH ][BH ]. These resulted, re-
Nitrogen N 19 33 (tie) 2 4
spectively, from symmetric cleavage of B 2 H 6 (BH 3 +
Gallium Ga 19 33 (tie) + −
BH 3 ) and unsymmetric cleavage of B 2 H 6 (BH + BH ).
Lead Pb 13 36 2 4
Many studies have shown that Lewis acid–base
Boron B 9 38
(BH 3 · base) products are common in borane chemistry
Tin Sn 2.1 48 (tie with europium)
due to the electron-deficient nature of boron. Phosphorus,
Arsenic As 1.8 51
arsenic, oxygen, and sulfur acid–base adducts are all
Germanium Ge 1.5 53
known. Borane (BH 3 ) is commonly stored and marketed
Thallium Tl 0.7 58
as its tetrahydrofuran adduct.
Indium In 0.24 61
Among the compounds that contain B N bonds, two
Antimony Sb 0.20 62
of them, boron nitride (BN) and borazole (B 3 N 3 H 6 ), merit
Selenium Se 0.05 66
special mention because of their resemblance to familiar
Bismuth Bi 0.008 69
carbon species. Boron nitride, a white, crystalline solid,
Tellurium Te 0.001 72 (tie with iridium)
has been compared to graphite because the layer structures