Page 197 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd InOrganic Chemistry
P. 197
P1: GSS Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN009F-398 July 6, 2001 20:34
6 Main Group Elements
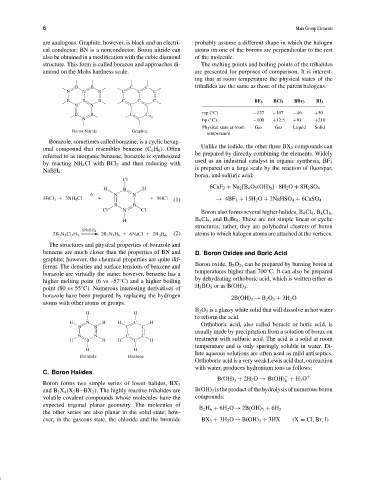
are analogous. Graphite, however, is black and an electri- probably assume a different shape in which the halogen
cal conductor; BN is a nonconductor. Boron nitride can atoms on one of the borons are perpendicular to the rest
also be obtained in a modification with the cubic diamond of the molecule.
structure. This form is called borazon and approaches di- The melting points and boiling points of the trihalides
amond on the Mohs hardness scale. are presented for purposes of comparison. It is interest-
ing that at room temperature the physical states of the
B B C C trihalides are the same as those of the parent halogens.
N N N C C C
B B B C C C BF 3 BCl 3 BBr 3 BI 3
N N C C
◦
B B C C mp ( C) −127 −107 −46 +50
N C bp ( C) −100 +12.5 +91 +210
◦
Physical state at room Gas Gas Liquid Solid
Boron Nitride Graphite
temperature
Borazole, sometimes called borazine, is a cyclic hexag-
Unlike the iodide, the other three BX 3 compounds can
onal compound that resembles benzene (C 6 H 6 ). Often
be prepared by directly combining the elements. Widely
referred to as inorganic benzene, borazole is synthesized
by reacting NH 4 Cl with BCl 3 and then reducing with used as an industrial catalyst in organic synthesis, BF 3
is prepared on a large scale by the reaction of fluorspar,
NaBH 4 :
borax, and sulfuric acid:
Cl
H B H 6CaF 2 + Na 2 [B 4 O 5 (OH) ] · 8H 2 O + 8H 2 SO 4
5
N N
3BCl 3 3NH 4 Cl 9HCl (1) → 4BF 3 + 15H 2 O + 2NaHSO 4 + 6CaSO 4
B B
Cl N Cl
Boron also forms several higher halides, B 4 Cl 4 ,B 8 Cl 8 ,
H B 9 Cl 9 , and B 9 Br 9 . These are not simple linear or cyclic
structures; rather, they are polyhedral clusters of boron
6NaBH 4
(2) atoms to which halogen atoms are attached at the vertices.
2B 3 N 3 Cl 3 H 3 2B 3 N 3 H 6 6NaCl 2B 2 H 6
The structures and physical properties of borazole and
benzene are much closer than the properties of BN and D. Boron Oxides and Boric Acid
graphite; however, the chemical properties are quite dif-
Boron oxide, B 2 O 3 , can be prepared by burning boron at
ferent. The densities and surface tensions of benzene and
◦
temperatures higher than 700 C. It can also be prepared
borazole are virtually the same; however, benzene has a
by dehydrating orthoboric acid, which is written either as
◦
higher melting point (6 vs –57 C) and a higher boiling
H 3 BO 3 or as B(OH) 3 :
point (80 vs 55 C). Numerous interesting derivatives of
◦
borazole have been prepared by replacing the hydrogen
2B(OH) → B 2 O 3 + 3H 2 O
3
atoms with other atoms or groups.
B 2 O 3 is a glassy white solid that will dissolve in hot water
H H
to reform the acid.
H N H H C H Orthoboric acid, also called boracic or boric acid, is
B B C C
usually made by precipitation from a solution of borax on
N N C C
H B H H C H treatment with sulfuric acid. The acid is a solid at room
temperature and is only sparingly soluble in water. Di-
H H
lute aqueous solutions are often used as mild antiseptics.
Borazole Benzene
Orthoboric acid is a very weak Lewis acid that, on reaction
with water, produces hydronium ions as follows:
C. Boron Halides
−
B(OH) + 2H 2 O → B(OH) + H 3 O +
3
4
Boron forms two simple series of lower halides, BX 3
and B 2 X 4 (X 2 B BX 2 ). The highly reactive trihalides are B(OH) 3 is the product of the hydrolysis of numerous boron
volatile covalent compounds whose molecules have the compounds:
expected trigonal planar geometry. The molecules of
3
B 2 H 6 + 6H 2 O→2B(OH) + 6H 2
the other series are also planar in the solid state; how-
ever, in the gaseous state, the chloride and the bromide BX 3 + 3H 2 O→B(OH) + 3HX (X = Cl, Br, I)
3