Page 227 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd InOrganic Chemistry
P. 227
P1: GPB Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN009I-420 July 10, 2001 15:8
374 Mesoporous Materials, Synthesis and Properties
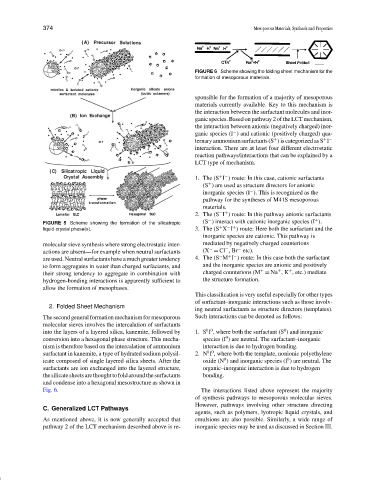
FIGURE 6 Scheme showing the folding sheet mechanism for the
formation of mesoporous materials.
sponsible for the formation of a majority of mesoporous
materials currently available. Key to this mechanism is
the interaction between the surfactant molecules and inor-
ganic species. Based on pathway 2 of the LCT mechanism,
the interaction between anionic (negatively charged) inor-
ganic species (I ) and cationic (positively charged) qua-
−
ternary ammonium surfactants (S ) is categorized as S I
+
+ −
interaction. There are at least four different electrostatic
reaction pathways/interactions that can be explained by a
LCT type of mechanism.
1. The (S I ) route: In this case, cationic surfactants
+ −
(S ) are used as structure directors for anionic
+
inorganic species (I ). This is recognized as the
−
pathway for the syntheses of M41S mesoporous
materials.
2. The (S I ) route: In this pathway anionic surfactants
− +
−
+
FIGURE 5 Scheme showing the formation of the silicatropic (S ) interact with cationic inorganic species (I ).
− +
+
liquid-crystal phase(s). 3. The (S X I ) route: Here both the surfactant and the
inorganic species are cationic. This pathway is
molecular sieve synthesis where strong electrostatic inter- mediated by negatively charged counterions
−
−
−
actions are absent—for example when neutral surfactants (X = Cl ,Br etc).
+ −
−
are used. Neutral surfactants have a much greater tendency 4. The (S M I ) route: In this case both the surfactant
to form aggregates in water than charged surfactants, and and the inorganic species are anionic and positively
+
+
+
their strong tendency to aggregate in combination with charged counterions (M = Na ,K , etc.) mediate
hydrogen-bonding interactions is apparently sufficient to the structure formation.
allow the formation of mesophases.
This classification is very useful especially for other types
of surfactant–inorganic interactions such as those involv-
2. Folded Sheet Mechanism
ing neutral surfactants as structure directors (templates).
The second general formation mechanism for mesoporous Such interactions can be denoted as follows:
molecular sieves involves the intercalation of surfactants
0 0
0
into the layers of a layered silica, kanemite, followed by 1. S I , where both the surfactant (S ) and inorganic
0
conversion into a hexagonal phase structure. This mecha- species (I ) are neutral. The surfactant–inorganic
nism is therefore based on the intercalation of ammonium interaction is due to hydrogen bonding.
0 0
surfactant in kanemite, a type of hydrated sodium polysil- 2. N I , where both the template, nonionic polyethylene
0
0
icate composed of single layered silica sheets. After the oxide (N ) and inorganic species (I ) are neutral. The
surfactants are ion exchanged into the layered structure, organic–inorganic interaction is due to hydrogen
thesilicatesheetsarethoughttofoldaroundthesurfactants bonding.
and condense into a hexagonal mesostructure as shown in
Fig. 6. The interactions listed above represent the majority
of synthesis pathways to mesoporous molecular sieves.
However, pathways involving other structure directing
C. Generalized LCT Pathways
agents, such as polymers, lyotropic liquid crystals, and
As mentioned above, it is now generally accepted that emulsions are also possible. Similarly, a wide range of
pathway 2 of the LCT mechanism described above is re- inorganic species may be used as discussed in Section III.