Page 230 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd InOrganic Chemistry
P. 230
P1: GPB Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN009I-420 July 10, 2001 15:8
Mesoporous Materials, Synthesis and Properties 377
size. Changes in these synthesis parameters can be used
to tailor the pore size.
VI. CHARACTERIZATION TECHNIQUES
AND PROPERTIES
Many different techniques are used to characterize mes-
oporous materials. Often several techniques are used
in combination, in order to provide conclusive struc-
tural information. The most valuable methods for stru-
cture elucidation include powder x-ray diffraction (XRD),
transmission electron microscopy (TEM), scanning elec-
tron microscopy (SEM), and adsorption (porosity) mea-
surements.
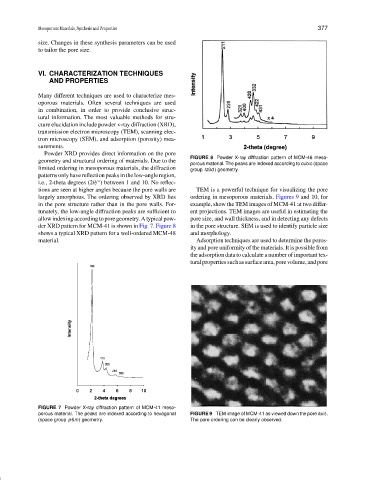
Powder XRD provides direct information on the pore
FIGURE 8 Powder X-ray diffraction pattern of MCM-48 meso-
geometry and structural ordering of materials. Due to the
porous material. The peaks are indexed according to cubic (space
limited ordering in mesoporous materials, the diffraction group Ia3d ) geometry.
patternsonlyhavereflectionpeaksinthelow-angleregion,
i.e., 2-theta degrees (2θ/ ) between 1 and 10. No reflec-
◦
tions are seen at higher angles because the pore walls are TEM is a powerful technique for visualizing the pore
largely amorphous. The ordering observed by XRD lies ordering in mesoporous materials. Figures 9 and 10, for
in the pore structure rather than in the pore walls. For- example, show the TEM images of MCM-41 at two differ-
tunately, the low-angle diffraction peaks are sufficient to ent projections. TEM images are useful in estimating the
allowindexingaccordingtoporegeometry.Atypicalpow- pore size, and wall thickness, and in detecting any defects
der XRD pattern for MCM-41 is shown in Fig. 7. Figure 8 in the pore structure. SEM is used to identify particle size
shows a typical XRD pattern for a well-ordered MCM-48 and morphology.
material. Adsorption techniques are used to determine the poros-
ity and pore uniformity of the materials. It is possible from
the adsorption data to calculate a number of important tex-
turalpropertiessuchassurfacearea,porevolume,andpore
FIGURE 7 Powder X-ray diffraction pattern of MCM-41 meso-
porous material. The peaks are indexed according to hexagonal FIGURE 9 TEM image of MCM-41 as viewed down the pore axis.
(space group p6m) geometry. The pore ordering can be clearly observed.