Page 233 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd InOrganic Chemistry
P. 233
P1: GPB Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN009I-420 July 10, 2001 15:8
380 Mesoporous Materials, Synthesis and Properties
cant catalytic improvement above that of conventional or
commercial catalysts. This is again due to the larger pore
size of mesoporous materials, which allow easy access of
reactants to the active ingredients and subsequent product
release. For transition metal modified mesoporous molec-
ular sieves, innovative applications dealing particularly
with bulky molecules relevant to fine chemical synthesis
are possible. Another important area is the deposition of
transition-metal complexes within the channels and cavi-
ties of mesoporous molecular sieves resulting in materials
that are likely to be useful as enzyme-mimicking catalysts.
B. Thin Films and Membranes—Separation
In order to be used in thin film or membrane applica-
tions, mesoporous materials must be manufactured in the
form of defect-free oriented thin films. These films should
have controllable pore directions as well as variable thick-
ness. Thin films of mesoporus materials can be grown
onto a substrate (e.g., mica) or at the interface between
air and water. A major disadvantage of unidimensional
mesoporous thin films is that their pores tend to be aligned
parallel to the substrate or interface that they are grown
at. In potential applications such as biomolecular separa-
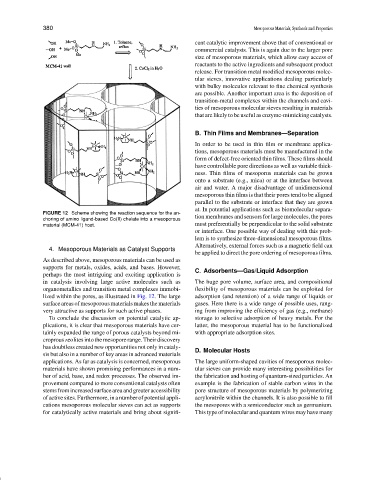
FIGURE 12 Scheme showing the reaction sequence for the an-
choring of amino ligand-based Co(II) chelate into a mesoporous tion membranes and sensors for large molecules, the pores
material (MCM-41) host. must preferentially be perpendicular to the solid substrate
or interface. One possible way of dealing with this prob-
lem is to synthesize three-dimensional mesoporous films.
Alternatively, external forces such as a magnetic field can
4. Mesoporous Materials as Catalyst Supports
be applied to direct the pore ordering of mesoporous films.
As described above, mesoporous materials can be used as
supports for metals, oxides, acids, and bases. However,
C. Adsorbents—Gas/Liquid Adsorption
perhaps the most intriguing and exciting application is
in catalysis involving large active molecules such as The huge pore volume, surface area, and compositional
organometallics and transition metal complexes immobi- flexibility of mesoporous materials can be exploited for
lized within the pores, as illustrated in Fig. 12. The large adsorption (and retention) of a wide range of liquids or
surface areas of mesoporous materials makes the materials gases. Here there is a wide range of possible uses, rang-
very attractive as supports for such active phases. ing from improving the efficiency of gas (e.g., methane)
To conclude the discussion on potential catalytic ap- storage to selective adsorption of heavy metals. For the
plications, it is clear that mesoporous materials have cer- latter, the mesoporous material has to be functionalized
tainly expanded the range of porous catalysts beyond mi- with appropriate adsorption sites.
croprous zeolites into the mesopore range. Their discovery
has doubtless created new opportunities not only in cataly- D. Molecular Hosts
sis but also in a number of key areas in advanced materials
applications. As far as catalysis is concerned, mesoporous The large uniform-shaped cavities of mesoporous molec-
materials have shown promising performances in a num- ular sieves can provide many interesting possibilities for
ber of acid, base, and redox processes. The observed im- the fabrication and hosting of quantum-sized particles. An
provement compared to more conventional catalysts often example is the fabrication of stable carbon wires in the
stems from increased surface area and greater accessibility pore structure of mesoporous materials by polymerizing
of active sites. Furthermore, in a number of potential appli- acrylonitrile within the channels. It is also possible to fill
cations mesoporous molecular sieves can act as supports the mesopores with a semiconductor such as germanium.
for catalytically active materials and bring about signifi- This type of molecular and quantum wires may have many