Page 26 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd InOrganic Chemistry
P. 26
P1: FYK Revised Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN001F-11 May 7, 2001 12:19
234 Actinide Elements
bipyramidal, and hexagonal bipyramidal geometries. The TABLE XIV Organometallic Actinide Compounds
actinyl group is linear with further coordination occur- a
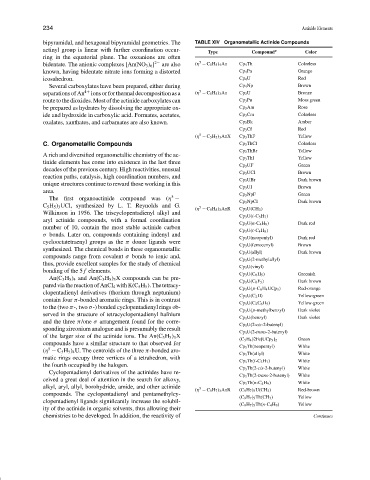
Type Compound Color
ring in the equatorial plane. The oxoanions are often
5
bidentate. The anionic complexes [An(NO 3 ) 6 ] 2− are also (η − C 5 H 5 ) 4 An Cp 4 Th Colorless
known, having bidentate nitrate ions forming a distorted Cp 4 Pa Orange
icosahedron. Cp 4 U Red
Several carboxylates have been prepared, either during Cp 4 Np Brown
5
separations of An 4+ ions or for thermal decomposition as a (η − C 5 H 5 ) 3 An Cp 3 U Bronze
route to the dioxides. Most of the actinide carboxylates can Cp 3 Pu Moss green
be prepared as hydrates by dissolving the appropriate ox- Cp 3 Am Rose
ide and hydroxide in carboxylic acid. Formates, acetates, Cp 3 Cm Colorless
oxalates, xanthates, and carbamates are also known. Cp 3 Bk Amber
Cp 3 Cf Red
5
(η − C 5 H 5 ) 3 AnX Cp 3 ThF Yellow
C. Organometallic Compounds Cp 3 ThCl Colorless
Cp 3 ThBr Yellow
A rich and diversified organometallic chemistry of the ac-
Cp 3 ThI Yellow
tinide elements has come into existence in the last three
Cp 3 UF Green
decades of the previous century. High reactivities, unusual
Cp 3 UCI Brown
reaction paths, catalysis, high coordination numbers, and
Cp 3 UBr Dark brown
unique structures continue to reward those working in this
Cp 3 UI Brown
area.
5 Cp 3 NpF Green
The first organoactinide compound was (η −
Cp 3 NpCI Dark brown
C 5 H 5 ) 3 UCl, synthesized by L. T. Reynolds and G.
5
(η − C 5 H 5 ) 3 AnR Cp 3 U(CH 3 )
Wilkinson in 1956. The triscyclopentadienyl alkyl and
Cp 3 U(i-C 3 H 7 )
aryl actinide compounds, with a formal coordination
Cp 3 U(n-C 4 H 9 ) Dark red
number of 10, contain the most stable actinide carbon
Cp 3 U(t-C 4 H 9 )
σ bonds. Later on, compounds containing indenyl and
Cp 3 U(neopentyl) Dark red
cyclooctatetraenyl groups as the π donor ligands were
Cp 3 U(ferrocenyl) Brown
synthesized. The chemical bonds in these organometallic
Cp 3 U(allyl) Dark brown
compounds range from covalent σ bonds to ionic and,
Cp 3 U(2-methylallyl)
thus, provide excellent samples for the study of chemical
Cp 3 U(vinyl)
bonding of the 5 f elements.
Cp 3 U(C 6 H 5 ) Greenish
An(C 5 H 5 ) 4 and An(C 5 H 5 ) 3 X compounds can be pre-
Cp 3 U(C 6 F 5 ) Dark brown
paredviathereactionofAnCl 4 withK(C 5 H 5 ).Thetetracy-
Cp 3 U(p-C 6 H 4 UCp 3 ) Red-orange
clopentadienyl derivatives (thorium through neptunium)
Cp 3 U(C 2 H) Yellow-green
contain four π-bonded aromatic rings. This is in contrast
Cp 3 U(C 2 C 6 H 5 ) Yellow-green
to the (two π-, two σ-) bonded cyclopentadienyl rings ob-
Cp 3 U(p-methylbenzyl) Dark violet
served in the structure of tetracyclopentadienyl hafnium
Cp 3 U(benzyl) Dark violet
and the three π/one σ arrangement found for the corre-
Cp 3 U(2-cis-2-butenyl)
sponding zirconium analogue and is presumably the result
Cp 3 U(2-trans-2-butenyl)
of the larger size of the actinide ions. The An(C 5 H 5 ) 3 X
(C 5 H 4 )2Fe[UCp 3 ] 2 Green
compounds have a similar structure to that observed for Cp 3 Th(neopentyl) White
5
(η − C 5 H 5 ) 4 U. The centroids of the three π-bonded aro-
Cp 3 Th(allyl) White
matic rings occupy three vertices of a tetrahedron, with
Cp 3 Th(i-C 3 H 7 ) White
the fourth occupied by the halogen.
Cp 3 Th(2-cis-2-butenyl) White
Cyclopentadienyl derivatives of the actinides have re-
Cp 3 Th(2-trans-2-butenyl) White
ceived a great deal of attention in the search for alkoxy,
Cp 3 Th(n-C 4 H 9 ) White
alkyl, aryl, allyl, borohydride, amide, and other actinide
5
(η − C 9 H 7 ) 3 AnR (C 9 H 7 ) 3 U(CH 3 ) Red-brown
compounds. The cyclopentadienyl and pentamethylcy-
(C 9 H 7 ) 3 Th(CH 3 ) Yellow
clopentadienyl ligands significantly increase the solubil-
(C 9 H 7 ) 3 Th(n-C 4 H 9 ) Yellow
ity of the actinide in organic solvents, thus allowing their
chemistries to be developed. In addition, the reactivity of Continues