Page 260 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd InOrganic Chemistry
P. 260
P1: GNH Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN009M-428 July 18, 2001 1:6
Metal Particles and Cluster Compounds 517
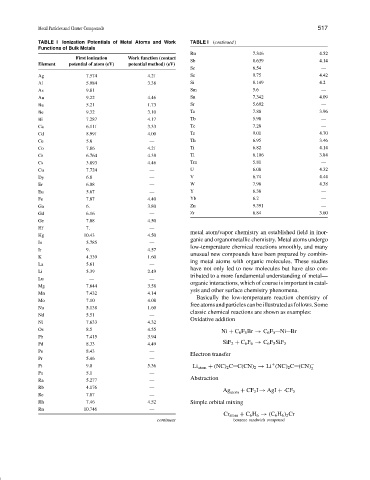
TABLE I Ionization Potentials of Metal Atoms and Work TABLE I (continued )
Functions of Bulk Metals
Ru 7.346 4.52
First ionization Work function (contact
Sb 8.639 4.14
Element potential of atom (eV) potential method) (eV)
Sc 6.54 —
Ag 7.574 4.21 Se 9.75 4.42
Al 5.984 3.38 Si 8.149 4.2
As 9.81 — Sm 5.6 —
Au 9.22 4.46 Sn 7.342 4.09
Ba 5.21 1.73 Sr 5.692 —
Be 9.32 3.10 Ta 7.88 3.96
Bi 7.287 4.17 Tb 5.98 —
Ca 6.111 3.33 Tc 7.28 —
Cd 8.991 4.00 Te 9.01 4.70
Ce 5.6 — Th 6.95 3.46
Co 7.86 4.21 Ti 6.82 4.14
Cr 6.764 4.38 Tl 6.106 3.84
Cs 3.893 4.46 Tm 5.81 —
Cu 7.724 — U 6.08 4.32
Dy 6.8 — V 6.74 4.44
Er 6.08 — W 7.98 4.38
Eu 5.67 — Y 6.38 —
Fe 7.87 4.40 Yb 6.2 —
Ga 6. 3.80 Zn 9.391 —
Gd 6.16 — Zr 6.84 3.60
Ge 7.88 4.50
Hf 7. —
metal atom/vapor chemistry an established field in inor-
Hg 10.43 4.50
ganic and organometallic chemistry. Metal atoms undergo
In 5.785 —
low-temperature chemical reactions smoothly, and many
Ir 9. 4.57
unusual new compounds have been prepared by combin-
K 4.339 1.60
ing metal atoms with organic molecules. These studies
La 5.61 —
have not only led to new molecules but have also con-
Li 5.39 2.49
tributed to a more fundamental understanding of metal—
Lu — —
organic interactions, which of course is important in catal-
Mg 7.644 3.58
ysis and other surface chemistry phenomena.
Mn 7.432 4.14
Basically the low-temperature reaction chemistry of
Mo 7.10 4.08
free atoms and particles can be illustrated as follows. Some
Na 5.138 1.60
classic chemical reactions are shown as examples:
Nd 5.51 —
Oxidative addition
Ni 7.633 4.32
Os 8.5 4.55
Ni + C 6 F 5 Br → C 6 F 5 Ni Br
Pb 7.415 3.94
Pd 8.33 4.49 SiF 2 + C 6 F 6 → C 6 F 5 SiF 3
Po 8.43 —
Electron transfer
Pr 5.46 —
+
Pt 9.0 5.36 Li atom + (NC) 2 C C(CN) 2 → Li (NC) 2 C (CN) −
2
Pu 5.1 —
Abstraction
Ra 5.277 —
Rb 4.176 —
Ag atom + CF 3 I → AgI +·CF 3
Re 7.87 —
Rh 7.46 4.52 Simple orbital mixing
Rn 10.746 —
Cr atom + C 6 H 6 → (C 6 H 6 ) 2 Cr
continues benzene sandwich compound