Page 274 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd InOrganic Chemistry
P. 274
P1: GNH Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN009M-428 July 18, 2001 1:6
Metal Particles and Cluster Compounds 531
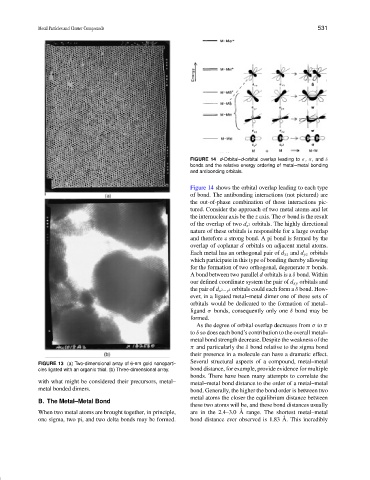
FIGURE 14 d-Orbital–d-orbital overlap leading to σ, π, and δ
bonds and the relative energy ordering of metal–metal bonding
and antibonding orbitals.
Figure 14 shows the orbital overlap leading to each type
of bond. The antibonding interactions (not pictured) are
the out-of-phase combination of those interactions pic-
tured. Consider the approach of two metal atoms and let
the internuclear axis be the z axis. The σ bond is the result
of the overlap of two d z orbitals. The highly directional
2
nature of these orbitals is responsible for a large overlap
and therefore a strong bond. A pi bond is formed by the
overlap of coplanar d orbitals on adjacent metal atoms.
Each metal has an orthogonal pair of d xz and d yz orbitals
which participate in this type of bonding thereby allowing
for the formation of two orthogonal, degenerate π bonds.
A bond between two parallel d orbitals is a δ bond. Within
our defined coordinate system the pair of d xy orbitals and
the pair of d x −y orbitals could each form a δ bond. How-
2
2
ever, in a ligated metal–metal dimer one of these sets of
orbitals would be dedicated to the formation of metal–
ligand σ bonds, consequently only one δ bond may be
formed.
As the degree of orbital overlap decreases from σ to π
to δ so does each bond’s contribution to the overall metal–
metal bond strength decrease. Despite the weakness of the
π and particularly the δ bond relative to the sigma bond
their presence in a molecule can have a dramatic effect.
Several structural aspects of a compound, metal–metal
FIGURE 13 (a) Two-dimensional array of 6-nm gold nanoparti-
cles ligated with an organic thiol. (b) Three-dimensional array. bond distance, for example, provide evidence for multiple
bonds. There have been many attempts to correlate the
with what might be considered their precursors, metal– metal–metal bond distance to the order of a metal–metal
metal bonded dimers. bond. Generally, the higher the bond order is between two
metal atoms the closer the equilibrium distance between
B. The Metal–Metal Bond
these two atoms will be, and these bond distances usually
˚
When two metal atoms are brought together, in principle, are in the 2.4–3.0 A range. The shortest metal–metal
˚
one sigma, two pi, and two delta bonds may be formed. bond distance ever observed is 1.83 A. This incredibly