Page 306 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd InOrganic Chemistry
P. 306
P1: GTV/GRI P2: GNH Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN010H-470 July 16, 2001 16:53
Nanosized Inorganic Clusters 315
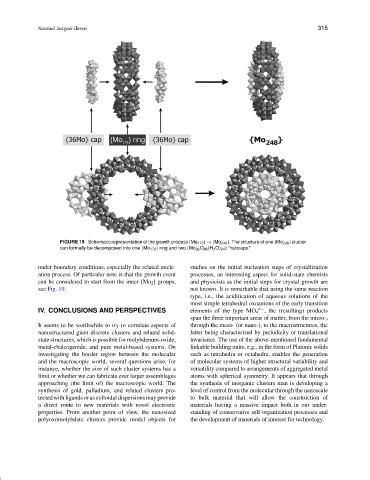
FIGURE 19 Schematic representation of the growth process {Mo 176 }→{Mo 248 }. The structure of one {Mo 248 } cluster
can formally be decomposed into one {Mo 176 } ring and two {Mo 36 O 96 (H 2 O) 24 } “hubcaps.”
under boundary conditions, especially the related nucle- studies on the initial nucleation steps of crystallization
ation process. Of particular note is that the growth event processes, an interesting aspect for solid-state chemists
can be considered to start from the inner {Mo 2 } groups, and physicists as the initial steps for crystal growth are
see Fig. 19. not known. It is remarkable that using the same reaction
type, i.e., the acidification of aqueous solutions of the
most simple tetrahedral oxoanions of the early transition
IV. CONCLUSIONS AND PERSPECTIVES elements of the type MO 4 n− , the (resulting) products
span the three important areas of matter, from the micro-,
It seems to be worthwhile to try to correlate aspects of through the meso- (or nano-), to the macrostructures, the
nanostructured giant discrete clusters and related solid- latter being characterized by periodicity or translational
state structures, which is possible for molybdenum-oxide, invariance. The use of the above-mentioned fundamental
metal-chalcogenide, and pure metal-based systems. On linkable building units, e.g., in the form of Platonic solids
investigating the border region between the molecular such as tetrahedra or octahedra, enables the generation
and the macroscopic world, several questions arise, for of molecular systems of higher structural variability and
instance, whether the size of such cluster systems has a versatility compared to arrangements of aggregated metal
limit or whether we can fabricate ever larger assemblages atoms with spherical symmetry. It appears that through
approaching (the limit of) the macroscopic world. The the synthesis of inorganic clusters man is developing a
synthesis of gold, palladium, and related clusters pro- level of control from the molecular through the nanoscale
tected with ligands or as colloidal dispersions may provide to bulk material that will allow the construction of
a direct route to new materials with novel electronic materials having a massive impact both in our under-
properties. From another point of view, the nanosized standing of conservative self-organization processes and
polyoxomolybdate clusters provide model objects for the development of materials of interest for technology.