Page 37 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd InOrganic Chemistry
P. 37
P1: ZBU Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN002F-55 May 22, 2001 21:6
Bioinorganic Chemistry 125
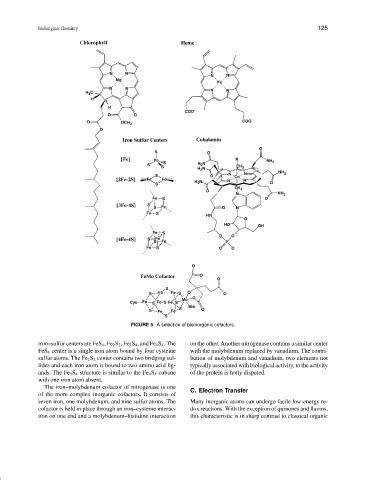
FIGURE 5 A selection of bioinorganic cofactors.
iron–sulfur centers are FeS 4 ,Fe 2 S 2 ,Fe 3 S 4 , and Fe 4 S 4 . The on the other. Another nitrogenase contains a similar center
FeS 4 center is a single iron atom bound by four cysteine with the molybdenum replaced by vanadium. The contri-
sulfur atoms. The Fe 2 S 2 center contains two bridging sul- bution of molybdenum and vanadium, two elements not
fides and each iron atom is bound to two amino acid lig- typically associated with biological activity, to the activity
ands. The Fe 3 S 4 structure is similar to the Fe 4 S 4 cubane of the protein is hotly disputed.
with one iron atom absent.
The iron–molybdenum cofactor of nitrogenase is one C. Electron Transfer
of the more complex inorganic cofactors. It consists of
seven iron, one molybdenum, and nine sulfur atoms. The Many inorganic atoms can undergo facile low-energy re-
cofactor is held in place through an iron–cysteine interac- dox reactions. With the exception of quinones and flavins,
tion on one end and a molybdenum–histidine interaction this characteristic is in sharp contrast to classical organic