Page 58 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd InOrganic Chemistry
P. 58
P1: LLL Revised Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN002c-73 May 21, 2001 13:59
Boron Hydrides 307
H H H H H H
H H H H H H
B B B B B B B B
H
B
H H H H B H H H H H B H
B
H
B B B B B B B B
H H H H H H
H H H H H H
Acombinationorresonancehybridofthesefourstructures 1. The total number of three-center bonds will equal the
produces a more symmetrical molecule where all of the number of boron atoms minus the charge because
four borons around the base of the square pyramid are each extra electron in the charge will lower the
equivalent. This is in agreement with the known structure. electron deficiency by one.
As boron hydrides get larger or more symmetrical, the
s + t = p − c
numbers of individual structures making up the hybrid get
to the point where it is essentially unmanageable. For these 2. The hydrogen atom balance will be the same as for
molecules the molecular orbital theory, which constructs the neutral boron hydrides.
orbitals for bonding from the atomic orbitals of multiple
s + x = q
atoms, is appropriate.
3. The electron balance now must include the electrons
imparting the charge. Besides the p pairs of electrons
IV. ISOELECTRONIC COMPOUNDS: from the B H groups, each negative charge results in
BORON HYDRIDE ANIONS one-half a pair more of electrons that are available for
AND CARBORANES the s, t, y, and x structural features.
c q
p + = t + y +
We will consider two important groups of compounds that 2 2
share the same kinds of geometries as boron hydrides, that The solution of these equations for the BH ion are
−
4
is, can be viewed as polyhedra or polyhedral fragments. s = 0, t = 0, y = 0, since none of these features is possible
These are the boron hydride anions and carboranes. In withasingleboronatom,and x = 3.Thisisastructurewith
many cases the boron hydrides and compounds in these no three-center bonds or boron-boron two-center bonds
groups are isoelectronic (same number of valence elec- and with three extra terminal hydrogen atoms on the single
trons), and in these cases the structures are isostructural boron atom.
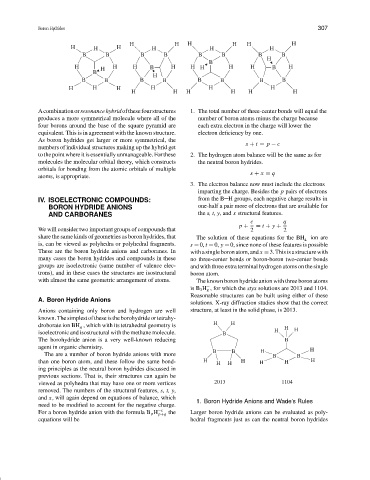
with almost the same geometric arrangement of atoms. The known boron hydride anion with three boron atoms
−
is B 3 H , for which the styx solutions are 2013 and 1104.
8
Reasonable structures can be built using either of these
A. Boron Hydride Anions
solutions. X-ray diffraction studies show that the correct
Anions containing only boron and hydrogen are well structure, at least in the solid phase, is 2013.
known. The simplest of these is the borohydride or tetrahy-
−
droborate ion BH , which with its tetrahedral geometry is H H
4 H H
isoelectronic and isostructural with the methane molecule. B H
The borohydride anion is a very well-known reducing B
agent in organic chemistry.
B B H H
The are a number of boron hydride anions with more B B
than one boron atom, and these follow the same bond- H H H H H H H
ing principles as the neutral boron hydrides discussed in
previous sections. That is, their structures can again be
viewed as polyhedra that may have one or more vertices 2013 1104
removed. The numbers of the structural features, s, t, y,
and x, will again depend on equations of balance, which
1. Boron Hydride Anions and Wade’s Rules
need to be modified to account for the negative charge.
For a boron hydride anion with the formula B p H −c the Larger boron hydride anions can be evaluated as poly-
p+q
equations will be hedral fragments just as can the neutral boron hydrides