Page 73 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd InOrganic Chemistry
P. 73
P1: FQP/LPB P2: FQP Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN003D-147 June 13, 2001 22:58
744 Coordination Compounds
The phenomena are closely akin to the remarkable dis-
solution by aqueous solutions of beryllium and zinc salts
of their own water, insoluble oxides [Eq. (30)]:
2H 2 O + MO + 2M 2+ M 3 (OH) 3+ + H +
3
(M = Be, Zn) (30)
Indeed, whenever the coordination number of a simple
anion in a complex is greater than 1, there is an element
of “inverse complexing,” and interesting properties result.
The following are examples:
1. The “oxo-bridged” species, where either O 2− or
OH links two metal ions, as in [Cl 5 RuORuCl 5 ] ; Dur-
−
4−
rant’s anion [(O 4 C 2 ) 2 Co(OH, OH)Co(C 2 O 4 ) 2 ] ; or the
4−
famous Werner’s hexol [Co{(OH) 2 Co(NH 3 ) 4 } 3 ] . Such
6+
bridging ligands carry the symbol µ.
2. Halide bridges. These are common, so that there are The presence of chelate rings stabilizes a molecule, for
many species with two-coordinated halide ligands, as in example, in Eq. (32), where en = 1,2-diaminoethane:
Pt(II)–Cl–Pt(II), often in the same complex species as one-
coordinated “terminal halides.” The properties of the ter- [(H 2 O) 4 Ni(NH 3 ) 2 ] 2+ + en → [(H 2 O) 4 Ni(en)] 2+ + 2NH 3
minal and bridging halide ions are quite different.
(32)
Omitting ionic charges and the four water molecules that
E. Chelation
remain attached to the nickel ion throughout, we obtain
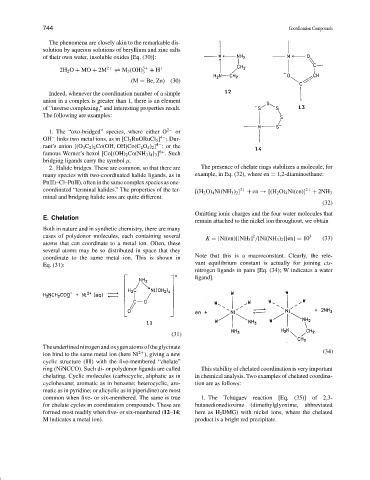
Both in nature and in synthetic chemistry, there are many
cases of polydonor molecules, each containing several 2 3
K = [Ni(en)][NH 3 ] /[Ni(NH 3 ) 2 ][en] = 10 (33)
atoms that can coordinate to a metal ion. Often, these
several atoms may be so distributed in space that they
coordinate to the same metal ion. This is shown in Note that this is a macroconstant. Clearly, the rele-
Eq. (31): vant equilibrium constant is actually for joining cis-
nitrogen ligands in pairs [Eq. (34); W indicates a water
ligand].
(31)
Theunderlinednitrogenandoxygenatomsoftheglycinate
(34)
ion bind to the same metal ion (here Ni ), giving a new
2+
cyclic structure (11) with the five-membered “chelate”
ring (NiNCCO). Such di- or polydonor ligands are called This stability of chelated coordination is very important
chelating. Cyclic molecules (carbocyclic, aliphatic as in in chemical analysis. Two examples of chelated coordina-
cyclohexane; aromatic as in benzene; heterocyclic, aro- tion are as follows:
matic as in pyridine; or alicyclic as in piperidine) are most
common when five- or six-membered. The same is true 1. The Tchugaev reaction [Eq. (35)] of 2,3-
for chelate cycles in coordination compounds. These are butanedionedioxime (dimethylglyoxime, abbreviated
formed most readily when five- or six-membered (12–14; here as H 2 DMG) with nickel ions, where the chelated
M indicates a metal ion). product is a bright red precipitate.