Page 56 - Subyek Encyclopedia - Encyclopedia of Separation Science
P. 56
Sepsci*21*TSK*Venkatachala=BG
I / CHROMATOGRAPHY 51
broadening resulting from radial temperature gradi-
ents. Separations in MEKC are typically carried out
with between 100 000 and 500 000 theoretical
plates. Adsorption of solutes on the column wall can
greatly reduce the potential column efRciency
and experimental conditions should be optimized to
minimize these contributions whenever possible.
Planar Chromatography
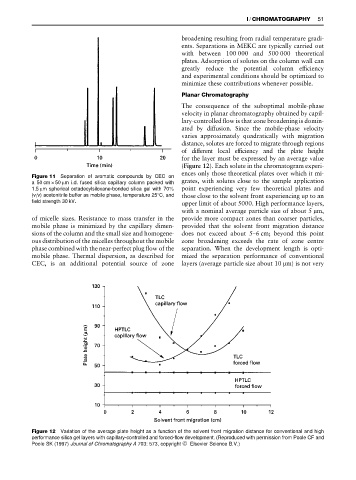
The consequence of the suboptimal mobile-phase
velocity in planar chromatography obtained by capil-
lary-controlled Sow is that zone broadening is domin-
ated by diffusion. Since the mobile-phase velocity
varies approximately quadratically with migration
distance, solutes are forced to migrate through regions
of different local efRciency and the plate height
for the layer must be expressed by an average value
(Figure 12). Each solute in the chromatogram experi-
ences only those theoretical plates over which it mi-
Figure 11 Separation of aromatic compounds by CEC on
grates, with solutes close to the sample application
a50 cm 50 m i.d. fused silica capillary column packed with
1.5 m spherical octadecylsiloxane-bonded silica gel with 70% point experiencing very few theoretical plates and
(v/v) acetonitrile buffer as mobile phase, temperature 253C, and those close to the solvent front experiencing up to an
field strength 30 kV.
upper limit of about 5000. High performance layers,
with a nominal average particle size of about 5 m,
of micelle sizes. Resistance to mass transfer in the provide more compact zones than coarser particles,
mobile phase is minimized by the capillary dimen- provided that the solvent front migration distance
sions of the column and the small size and homogene- does not exceed about 5}6 cm; beyond this point
ous distribution of the micelles throughout the mobile zone broadening exceeds the rate of zone centre
phase combined with the near-perfect plug Sow of the separation. When the development length is opti-
mobile phase. Thermal dispersion, as described for mized the separation performance of conventional
CEC, is an additional potential source of zone layers (average particle size about 10 m) is not very
Figure 12 Variation of the average plate height as a function of the solvent front migration distance for conventional and high
performance silica gel layers with capillary-controlled and forced-flow development. (Reproduced with permission from Poole CF and
Poole SK (1997) Journal of Chromatography A 703: 573, copyright ^ Elsevier Science B.V.)