Page 49 - Energy from Toxic Organic Waste for Heat and Power Generation
P. 49
Energy Extraction From Toxic Waste Originating From Food Processing Industries 37
place when the biomass burns (i.e., flaming mode) or when it is exposed to
elevated temperatures without burning (i.e., nonflaming mode). All com-
bustible materials, whether synthetic or man-made, generally produce toxic
products when burned. When biomass is heated under oxygen-deficient
conditions, it generates syngas, which consists primarily of hydrogen (H 2 )
and carbon monoxide (CO). This syngas can be directly burnt or further
processed for gaseous or liquid products, such as producer gas and pyro oil.
Low moisture content biomasses are more suitable for conversion processes
such as combustion, pyrolysis, and gasification [72]. The layout of energy
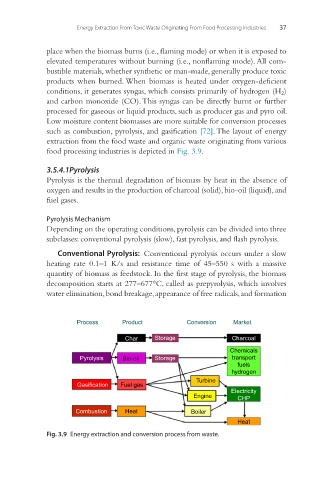
extraction from the food waste and organic waste originating from various
food processing industries is depicted in Fig. 3.9.
3.5.4.1Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is the thermal degradation of biomass by heat in the absence of
oxygen and results in the production of charcoal (solid), bio-oil (liquid), and
fuel gases.
Pyrolysis Mechanism
Depending on the operating conditions, pyrolysis can be divided into three
subclasses: conventional pyrolysis (slow), fast pyrolysis, and flash pyrolysis.
Conventional Pyrolysis: Conventional pyrolysis occurs under a slow
heating rate 0.1–1 K/s and resistance time of 45–550 s with a massive
quantity of biomass as feedstock. In the first stage of pyrolysis, the biomass
decomposition starts at 277–677°C, called as prepyrolysis, which involves
water elimination, bond breakage, appearance of free radicals, and formation
Process Product Conversion Market
Char Storage Charcoal
Chemicals
Pyrolysis Bio-oil Storage transport
fuels
hydrogen
Turbine
Gasification Fuel gas
Electricity
Engine CHP
Combustion Heat Boiler
Heat
Fig. 3.9 Energy extraction and conversion process from waste.