Page 48 - Energy from Toxic Organic Waste for Heat and Power Generation
P. 48
36 Energy from Toxic Organic Waste for Heat and Power Generation
50% fresh slurry along with 10% digested slurry can give about 50% water
conservation and 10% increase in biogas production.
3.5.4 Thermal Conversion of Food Waste
Due to the typically high-moisture content of food waste, combustion is
energy-intensive as shown in Fig. 3.2D. Food waste is, therefore, tradition-
ally combusted as a part of the MSW stream, where the energy for evap-
oration is provided by other combustible waste materials. Incineration
produces heat that can be converted into electricity. Produced ash (in-
combustible waste and air pollution control residues) is often landfilled,
but has some potential for reuse in construction and concrete. The
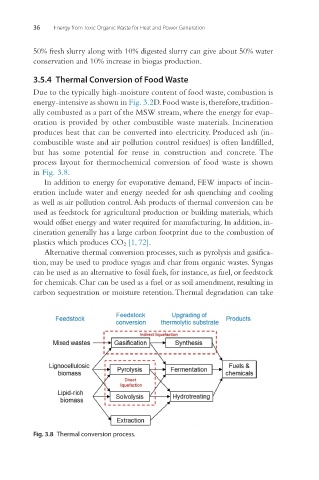
process layout for thermochemical conversion of food waste is shown
in Fig. 3.8.
In addition to energy for evaporative demand, FEW impacts of incin-
eration include water and energy needed for ash quenching and cooling
as well as air pollution control. Ash products of thermal conversion can be
used as feedstock for agricultural production or building materials, which
would offset energy and water required for manufacturing. In addition, in-
cineration generally has a large carbon footprint due to the combustion of
plastics which produces CO 2 [1, 72].
Alternative thermal conversion processes, such as pyrolysis and gasifica-
tion, may be used to produce syngas and char from organic wastes. Syngas
can be used as an alternative to fossil fuels, for instance, as fuel, or feedstock
for chemicals. Char can be used as a fuel or as soil amendment, resulting in
carbon sequestration or moisture retention. Thermal degradation can take
Fig. 3.8 Thermal conversion process.