Page 43 - Energy from Toxic Organic Waste for Heat and Power Generation
P. 43
Energy Extraction From Toxic Waste Originating From Food Processing Industries 31
C/N Ratio
It is necessary to maintain a proper composition of the feedstock for an
efficient operation of the biogas plant, so that the C/N ratio in the feed
remains within the desired range. Klassen et al. [54] reported that micro-
organisms utilize the carbon present in feedstock, 25–30 times faster than
nitrogen. Hence, to meet a favorable requirement for the microbes, the C
to N ratio must be in the range of 20–30:1. A higher C/N ratio than that
of the acceptable range gives an indication of the rapid consumption of ni-
trogen by methanogens and results in a lower gas production. On the other
hand, a lower C/N ratio causes ammonia accumulation and the pH value
exceeds 8.5, which is toxic to methanogenic bacteria. Optimum C/N ratios
of the feed materials can be achieved by mixing materials of high and low
C/N ratios. For example, a solid organic waste can be mixed with sewage
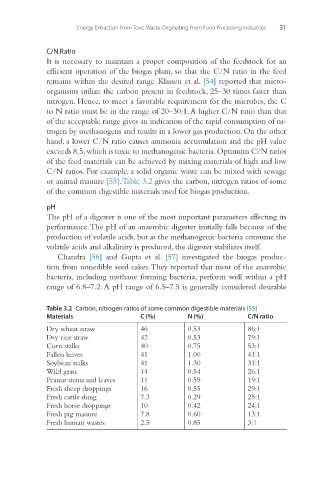
or animal manure [55]. Table 3.2 gives the carbon, nitrogen ratios of some
of the common digestible materials used for biogas production.
pH
The pH of a digester is one of the most important parameters affecting its
performance. The pH of an anaerobic digester initially falls because of the
production of volatile acids, but as the methanogenic bacteria consume the
volatile acids and alkalinity is produced, the digester stabilizes itself.
Chandra [56] and Gupta et al. [57] investigated the biogas produc-
tion from nonedible seed cakes. They reported that most of the anaerobic
bacteria, including methane forming bacteria, perform well within a pH
range of 6.8–7.2. A pH range of 6.5–7.5 is generally considered desirable
Table 3.2 Carbon, nitrogen ratios of some common digestible materials [55]
Materials C (%) N (%) C/N ratio
Dry wheat straw 46 0.53 86:1
Dry rice straw 42 0.53 79:1
Corn stalks 40 0.75 53:1
Fallen leaves 41 1.00 41:1
Soybean stalks 41 1.30 31:1
Wild grass 14 0.54 26:1
Peanut stems and leaves 11 0.59 19:1
Fresh sheep droppings 16 0.55 29:1
Fresh cattle dung 7.3 0.29 25:1
Fresh horse droppings 10 0.42 24:1
Fresh pig manure 7.8 0.60 13:1
Fresh human wastes 2.5 0.85 3:1