Page 40 - Energy from Toxic Organic Waste for Heat and Power Generation
P. 40
28 Energy from Toxic Organic Waste for Heat and Power Generation
Saxena et al. [36] and Balat and Demirbas [37] reported that, in the
biomass, the cellulose fraction is about 40%–50% by weight, whereas hemi-
cellulose is usually in the range of 20%–40% by weight, and lignin in the
range of 5%–30% by weight depending on the nature of the plant, whether
it is herbaceous or woody. All types of biomass consist of three polymers,
which are basically of cellulose (C 6 H 10 O 5 ) x , hemicellulose such as xylan
(C 5 H 8 O 4 ) m , and lignin [C 9 H 10 O 3 (OCH 3 ) 0.9–1.7 ] n . The proportion of these
polymers constitutes the difference between species, such as herbaceous
wood or soft wood (SW) and hard wood (HW). In general, soft wood
contains about 40%–44% cellulose, 25%–29% hemicellulose, 25%–31% lig-
nin, and 1%–5% extractives, while hard wood contains 43%–47% cellulose,
25%–35% hemicellulose, 16%–24% lignin, and 2%–8% extractives. The cel-
lulose, hemicellulose, and lignin contents in common agricultural residues
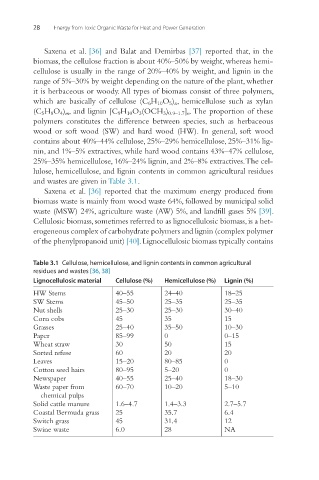
and wastes are given in Table 3.1.
Saxena et al. [36] reported that the maximum energy produced from
biomass waste is mainly from wood waste 64%, followed by municipal solid
waste (MSW) 24%, agriculture waste (AW) 5%, and landfill gases 5% [39].
Cellulosic biomass, sometimes referred to as lignocellulosic biomass, is a het-
erogeneous complex of carbohydrate polymers and lignin (complex polymer
of the phenylpropanoid unit) [40]. Lignocellulosic biomass typically contains
Table 3.1 Cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin contents in common agricultural
residues and wastes [36, 38]
Lignocellulosic material Cellulose (%) Hemicellulose (%) Lignin (%)
HW Stems 40–55 24–40 18–25
SW Stems 45–50 25–35 25–35
Nut shells 25–30 25–30 30–40
Corn cobs 45 35 15
Grasses 25–40 35–50 10–30
Paper 85–99 0 0–15
Wheat straw 30 50 15
Sorted refuse 60 20 20
Leaves 15–20 80–85 0
Cotton seed hairs 80–95 5–20 0
Newspaper 40–55 25–40 18–30
Waste paper from 60–70 10–20 5–10
chemical pulps
Solid cattle manure 1.6–4.7 1.4–3.3 2.7–5.7
Coastal Bermuda grass 25 35.7 6.4
Switch grass 45 31.4 12
Swine waste 6.0 28 NA