Page 38 - Energy from Toxic Organic Waste for Heat and Power Generation
P. 38
26 Energy from Toxic Organic Waste for Heat and Power Generation
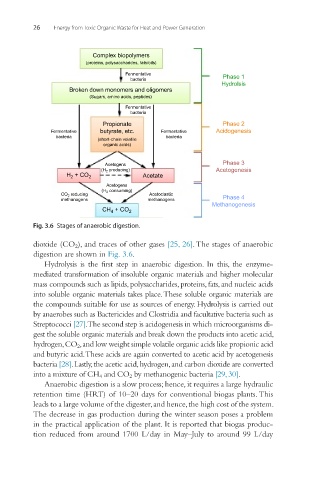
Complex biopolymers
(proteins, polysaccharides, fats/oils)
Fermentative
bacteria Phase 1
Hydrolsis
Broken down monomers and oligomers
(Sugars, amino acids, peptides)
Fermentative
bacteria
Propionate Phase 2
Fermentative butyrate, etc. Fermentative Acidogenesis
bacteria bacteria
(short-chain volatile
organic acids)
Acetogens Phase 3
(H 2 producing) Acetogenesis
H 2 + CO 2 Acetate
Acetogens
(H 2 consuming)
CO 2 reducing Acetoclastic
methanogens methanogens Phase 4
Methanogenesis
CH + CO 2
4
Fig. 3.6 Stages of anaerobic digestion.
dioxide (CO 2 ), and traces of other gases [25, 26]. The stages of anaerobic
digestion are shown in Fig. 3.6.
Hydrolysis is the first step in anaerobic digestion. In this, the enzyme-
mediated transformation of insoluble organic materials and higher molecular
mass compounds such as lipids, polysaccharides, proteins, fats, and nucleic acids
into soluble organic materials takes place. These soluble organic materials are
the compounds suitable for use as sources of energy. Hydrolysis is carried out
by anaerobes such as Bactericides and Clostridia and facultative bacteria such as
Streptococci [27]. The second step is acidogenesis in which microorganisms di-
gest the soluble organic materials and break down the products into acetic acid,
hydrogen, CO 2 , and low weight simple volatile organic acids like propionic acid
and butyric acid. These acids are again converted to acetic acid by acetogenesis
bacteria [28]. Lastly, the acetic acid, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide are converted
into a mixture of CH 4 and CO 2 by methanogenic bacteria [29, 30].
Anaerobic digestion is a slow process; hence, it requires a large hydraulic
retention time (HRT) of 10–20 days for conventional biogas plants. This
leads to a large volume of the digester, and hence, the high cost of the system.
The decrease in gas production during the winter season poses a problem
in the practical application of the plant. It is reported that biogas produc-
tion reduced from around 1700 L/day in May–July to around 99 L/day