Page 34 - Energy from Toxic Organic Waste for Heat and Power Generation
P. 34
22 Energy from Toxic Organic Waste for Heat and Power Generation
boundary conditions (e.g., generation rate). Additionally, the potential for
recycling food waste constituents to recover energy and nutrients creates
potential for nonlinear relationships between fluxes of food waste, energy,
and water. Characterizing the complex problem of postdisposal FEW nexus
impacts of wasted food, including descriptions of dynamic feedback behav-
iors, presents a significant research gap and a priority for future research.
Energy and water consumption and offsets associated with food waste man-
agement alternatives are as below:
(a) Composting
(b) Landfill
(c) Anaerobic digestion
(d) Thermal conversion
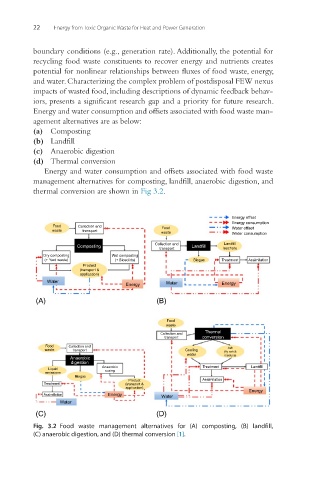
Energy and water consumption and offsets associated with food waste
management alternatives for composting, landfill, anaerobic digestion, and
thermal conversion are shown in Fig 3.2.
Energy offset
Energy consumption
Food Collection and
Food
waste transport waste Water offset
Water consumption
Collection and Landfill
Composting Landfill
transport leachate
Dry composting Wet composting
(+ Yard waste) (+ Biosolids) Biogas Treatment Assimilation
Product
(transport &
application)
Water Water Energy
Energy
(A) (B)
Food
waste
Thermal
Collection and
transport conversion
Food Collection and
Ash
waste transport Cooling (fly ash &
water residues)
Anaerobic
digestion
Anaerobic Treatment Landfill
Liquid curing
emissions
Biogas
Product Assimilation
Treatment (transport &
application) Energy
Assimilation Energy Water
Water
(C) (D)
Fig. 3.2 Food waste management alternatives for (A) composting, (B) landfill,
(C) anaerobic digestion, and (D) thermal conversion [1].