Page 194 - Engineered Interfaces in Fiber Reinforced Composites
P. 194
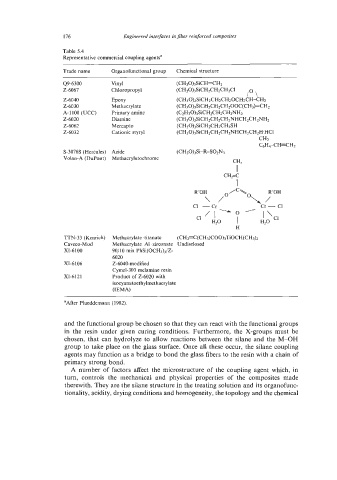
176 Engineered interfaces in fiber reinforced composites
Table 5.4
Representative commercial coupling agentsa
Trade name Organofunctional group Chemical structure
49-6300 Vinyl (CH30)3SiCH=CH2
2-6067 Chloropropyl (CH30)3SiCH2CH2CH2CI
lo \
2-6040 Epoxy (CH~O)~S~CH~CH~CHZOCH~CH-CH~
2-6030 Methacrylate (CH30)3SiCH2CH2CH200C(CH3)=CH2
A-1 100 (UCC) Primary amine (C2H30)3SiCH2CH2CH2NH2
2-6020 Diamine (CH30)3SiCH2CH2CH2NHCH2CHzNHz
2-6062 Mercapto (CH30)3SiCH2CH2CH2SH
2-6032 Cationic styryl (CH30)3SiCH2CH2CH2NHCH,CH2H.HC1
CH2
C6He-CH=CH*
S-3076s (Hercules) Azide ( CH30)3Si-R-S02N3
Volan-A (DuPont) Methacrylatochromc
C”,
I
CH,=C
I
R’OH
\/
CI
Cr
CI - Cr -
c1 / p O I ’ I ‘a
H,O HP
H
TTN-33 (Kenrich) Methacrylate-titanate (CH~=C(CH~)COO)~T~OCH(CH~)Z
Caveco-Mod Methacrylate-AI-zirconate Undisclosed
XI-6 100 90jlO mix PhSi(OCH3)3/2-
6020
XI-6106 2-6040-modified
Cymel-303 melamine resin
XI-6121 Product of 2-6020 with
isocyanatoethy lmethacrylate
(IEMA)
aAfter Plueddemann (1982).
and the functional group be chosen so that they can react with the functional groups
in the resin under given curing conditions. Furthermore, the X-groups must be
chosen, that can hydrolyze to allow reactions between the silane and the M-OH
group to take place on the glass surface. Once all these occur, the silane coupling
agents may function as a bridge to bond the glass fibers to the resin with a chain of
primary strong bond.
A number of factors affect the microstructure of the coupling agent which, in
turn, controls the mechanical and physical properties of the composites made
therewith. They are the silane structure in the treating solution and its organofunc-
tionality, acidity, drying conditions and homogeneity, the topology and the chemical