Page 192 - Engineered Interfaces in Fiber Reinforced Composites
P. 192
174 Engineered interfaces in fiber reinforced composites
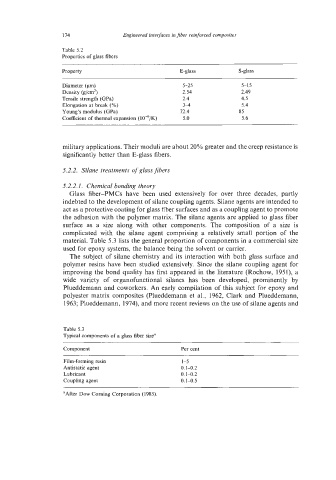
Table 5.2
Properties of glass fibers
Property E-glass S-glass
Diameter (pm) 5-25 515
Density (g/cm3) 2.54 2.49
Tensile strength (GPa) 2.4 4.5
Elongation at break (%) 34 5.4
Young’s modulus (GPa) 12.4 85
Coefficient of thermal expansion (10-6/K) 5.0 5.6
military applications. Their moduli are about 20% greater and the creep resistance is
significantly better than E-glass fibers.
5.2.2. Silane treatments of glass $fibers
5.2.2.1. Chemical bonding theory
Glass fiber-PMCs have been used extensively for over three decades, partly
indebted to the development of silane coupling agents. Silane agents are intended to
act as a protective coating for glass fiber surfaces and as a coupling agent to promote
the adhesion with the polymer matrix. The silane agents are applied to glass fiber
surface as a size along with other components. The composition of a size is
complicated with the silane agent comprising a relatively small portion of the
material. Table 5.3 lists the general proportion of components in a commercial size
used for epoxy systems, the balance being the solvent or carrier.
The subject of silane chemistry and its interaction with both glass surface and
polymer resins have been studied extensively. Since the silane coupling agent for
improving the bond quality has first appeared in the literature (Rochow, 1951), a
wide variety of organofunctional silanes has been developed, prominently by
Plueddemann and coworkers. An early compilation of this subject for epoxy and
polyester matrix composites (Plueddemann et al., 1962, Clark and Plueddemann,
1963; Plueddemann, 1974), and more recent reviews on the use of silane agents and
Table 5.3
Typical components of a glass fiber size“
Component Per cent
Film-forming resin 1-5
Antistatic agent 0.1-0.2
Lubricant 0.1-0.2
Coupling agent 0.1-0.5
“After Dow Corning Corporation (1985).