Page 138 - Engineering Digital Design
P. 138
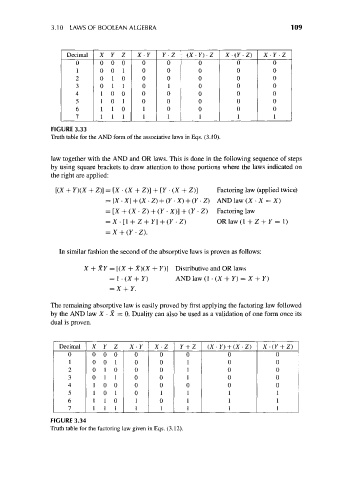
3.10 LAWS OF BOOLEAN ALGEBRA 109
Decimal X Y Z X-Y F- Z (X-Y)- Z X-(Y-Z) X-Y -Z
0 00 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
2 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
3 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0
4 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
5 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
6 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0
7 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
FIGURE 3.33
Truth table for the AND form of the associative laws in Eqs. (3.10).
law together with the AND and OR laws. This is done in the following sequence of steps
by using square brackets to draw attention to those portions where the laws indicated on
the right are applied:
[(X + Y)(X + Z)] = [X • (X + Z)] + [Y • (X + Z)] Factoring law (applied twice)
= [X • X] + (X • Z) + (Y • X) + (Y • Z) AND law (X • X = X)
= [X + (X • Z) + (Y • X)] + (Y • Z) Factoring law
In similar fashion the second of the absorptive laws is proven as follows:
X + XY = [(X + X)(X + Y)] Distributive and OR laws
= 1 • (X + Y) AND law (1 • (X + Y) = X + Y)
= X + Y.
The remaining absorptive law is easily proved by first applying the factoring law followed
by the AND law X • X = 0. Duality can also be used as a validation of one form once its
dual is proven.
Decimal X Y Z X • Y X • Z Y + Z (X - F) + (X • Z) X • (Y + Z)
0 00 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0
2 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0
3 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0
4 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
5 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1
6 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1
7 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
FIGURE 3.34
Truth table for the factoring law given in Eqs. (3.12).