Page 287 - Engineering Plastics Handbook
P. 287
Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP) 249
80
Weld strength at 1-mm thickness, MPa 65 W
75
70
60
55
50
45
40
35
30
SIVERAS ® Other Other
LX series LCP(A) LCP(B)
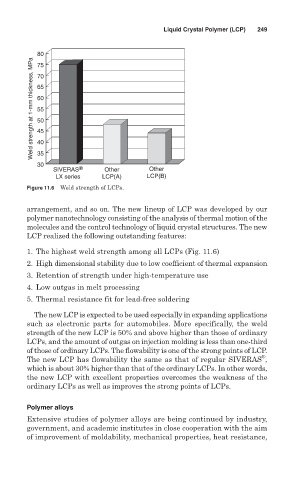
Figure 11.6 Weld strength of LCPs.
arrangement, and so on. The new lineup of LCP was developed by our
polymer nanotechnology consisting of the analysis of thermal motion of the
molecules and the control technology of liquid crystal structures. The new
LCP realized the following outstanding features:
1. The highest weld strength among all LCPs (Fig. 11.6)
2. High dimensional stability due to low coefficient of thermal expansion
3. Retention of strength under high-temperature use
4. Low outgas in melt processing
5. Thermal resistance fit for lead-free soldering
The new LCP is expected to be used especially in expanding applications
such as electronic parts for automobiles. More specifically, the weld
strength of the new LCP is 50% and above higher than those of ordinary
LCPs, and the amount of outgas on injection molding is less than one-third
of those of ordinary LCPs. The flowability is one of the strong points of LCP.
®
The new LCP has flowability the same as that of regular SIVERAS ,
which is about 30% higher than that of the ordinary LCPs. In other words,
the new LCP with excellent properties overcomes the weakness of the
ordinary LCPs as well as improves the strong points of LCPs.
Polymer alloys
Extensive studies of polymer alloys are being continued by industry,
government, and academic institutes in close cooperation with the aim
of improvement of moldability, mechanical properties, heat resistance,