Page 50 - Enhanced Oil Recovery in Shale and Tight Reservoirs
P. 50
38 Enhanced Oil Recovery in Shale and Tight Reservoirs
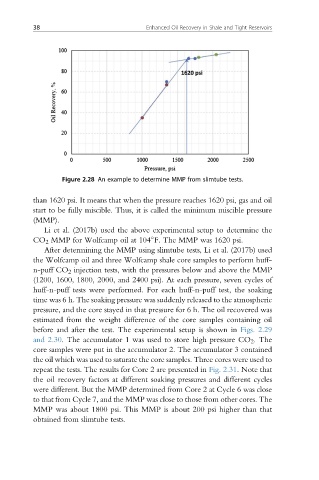
Figure 2.28 An example to determine MMP from slimtube tests.
than 1620 psi. It means that when the pressure reaches 1620 psi, gas and oil
start to be fully miscible. Thus, it is called the minimum miscible pressure
(MMP).
Li et al. (2017b) used the above experimental setup to determine the
CO 2 MMP for Wolfcamp oil at 104 F. The MMP was 1620 psi.
After determining the MMP using slimtube tests, Li et al. (2017b) used
the Wolfcamp oil and three Wolfcamp shale core samples to perform huff-
n-puff CO 2 injection tests, with the pressures below and above the MMP
(1200, 1600, 1800, 2000, and 2400 psi). At each pressure, seven cycles of
huff-n-puff tests were performed. For each huff-n-puff test, the soaking
time was 6 h. The soaking pressure was suddenly released to the atmospheric
pressure, and the core stayed in that pressure for 6 h. The oil recovered was
estimated from the weight difference of the core samples containing oil
before and after the test. The experimental setup is shown in Figs. 2.29
and 2.30. The accumulator 1 was used to store high pressure CO 2 . The
core samples were put in the accumulator 2. The accumulator 3 contained
the oil which was used to saturate the core samples. Three cores were used to
repeat the tests. The results for Core 2 are presented in Fig. 2.31. Note that
the oil recovery factors at different soaking pressures and different cycles
were different. But the MMP determined from Core 2 at Cycle 6 was close
to that from Cycle 7, and the MMP was close to those from other cores. The
MMP was about 1800 psi. This MMP is about 200 psi higher than that
obtained from slimtube tests.