Page 130 -
P. 130
106 Chapter 4 • Development Life Cycle
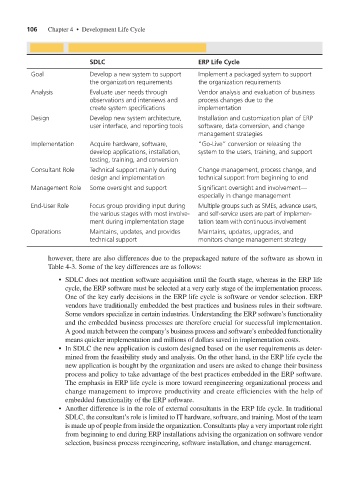
TABLE 4-3 Comparing and Contrasting SDLC with ERPLC
SDLC ERP Life Cycle
Goal Develop a new system to support Implement a packaged system to support
the organization requirements the organization requirements
Analysis Evaluate user needs through Vendor analysis and evaluation of business
observations and interviews and process changes due to the
create system specifications implementation
Design Develop new system architecture, Installation and customization plan of ERP
user interface, and reporting tools software, data conversion, and change
management strategies
Implementation Acquire hardware, software, “Go-Live” conversion or releasing the
develop applications, installation, system to the users, training, and support
testing, training, and conversion
Consultant Role Technical support mainly during Change management, process change, and
design and implementation technical support from beginning to end
Management Role Some oversight and support Significant oversight and involvement—
especially in change management
End-User Role Focus group providing input during Multiple groups such as SMEs, advance users,
the various stages with most involve- and self-service users are part of implemen-
ment during implementation stage tation team with continuous involvement
Operations Maintains, updates, and provides Maintains, updates, upgrades, and
technical support monitors change management strategy
however, there are also differences due to the prepackaged nature of the software as shown in
Table 4-3. Some of the key differences are as follows:
•SDLC does not mention software acquisition until the fourth stage, whereas in the ERP life
cycle, the ERP software must be selected at a very early stage of the implementation process.
One of the key early decisions in the ERP life cycle is software or vendor selection. ERP
vendors have traditionally embedded the best practices and business rules in their software.
Some vendors specialize in certain industries. Understanding the ERP software’s functionality
and the embedded business processes are therefore crucial for successful implementation.
A good match between the company’s business process and software’s embedded functionality
means quicker implementation and millions of dollars saved in implementation costs.
•In SDLC the new application is custom designed based on the user requirements as deter-
mined from the feasibility study and analysis. On the other hand, in the ERP life cycle the
new application is bought by the organization and users are asked to change their business
process and policy to take advantage of the best practices embedded in the ERP software.
The emphasis in ERP life cycle is more toward reengineering organizational process and
change management to improve productivity and create efficiencies with the help of
embedded functionality of the ERP software.
•Another difference is in the role of external consultants in the ERP life cycle. In traditional
SDLC, the consultant’s role is limited to IT hardware, software, and training. Most of the team
is made up of people from inside the organization. Consultants play a very important role right
from beginning to end during ERP installations advising the organization on software vendor
selection, business process reengineering, software installation, and change management.