Page 206 - Environmental Nanotechnology Applications and Impacts of Nanomaterials
P. 206
Reactive Oxygen Species Generation on Nanoparticulate Material 191
86
87
83
80
82 or 83
97 98 94 103
104
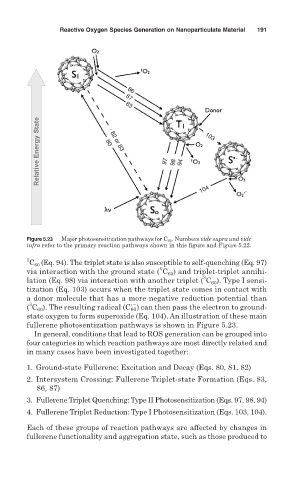
Figure 5.23 Major photosensitization pathways for C 60 . Numbers vide supra and vide
infra refer to the primary reaction pathways shown in this figure and Figure 5.22.
1
C (Eq. 94). The triplet state is also susceptible to self-quenching (Eq. 97)
60
0
via interaction with the ground state ( C ) and triplet-triplet annihi-
60
3
lation (Eq. 98) via interaction with another triplet ( C ). Type I sensi-
60
tization (Eq. 103) occurs when the triplet state comes in contact with
a donor molecule that has a more negative reduction potential than
3 ?2
( C ). The resulting radical (C 60 ) can then pass the electron to ground-
60
state oxygen to form superoxide (Eq. 104). An illustration of these main
fullerene photosentization pathways is shown in Figure 5.23.
In general, conditions that lead to ROS generation can be grouped into
four categories in which reaction pathways are most directly related and
in many cases have been investigated together:
1. Ground-state Fullerene: Excitation and Decay (Eqs. 80, 81, 82)
2. Intersystem Crossing: Fullerene Triplet-state Formation (Eqs. 83,
86, 87)
3. Fullerene Triplet Quenching: Type II Photosensitization (Eqs. 97, 98, 94)
4. Fullerene Triplet Reduction: Type I Photosensitization (Eqs. 103, 104).
Each of these groups of reaction pathways are affected by changes in
fullerene functionality and aggregation state, such as those produced to