Page 353 - Excel for Scientists and Engineers: Numerical Methods
P. 353
330 EXCEL: NUMERICAL METHODS
In biochemistry, the reaction rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction of a
substrate as a function of the concentration of the substrate is described by the
Michaelis-Menten equation,
( 14-7)
where V is the reaction velocity (typical units mmolh), K, is the Michaelis-
Menten constant (typical units mM), V,,, is the maximum reaction velocity and
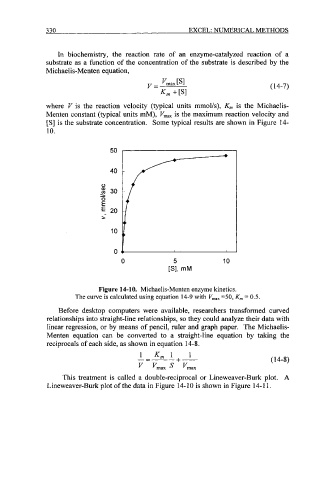
[S] is the substrate concentration. Some typical results are shown in Figure 14-
10.
50
40
0
% 30
L
E
E 20
J
10
Figure 14-10. Michaelis-Menten enzyme kinetics.
The curve is calculated using equation 14-9 with V,,, =50, K,,, = 0.5.
Before desktop computers were available, researchers transformed curved
relationships into straight-line relationships, so they could analyze their data with
linear regression, or by means of pencil, ruler and graph paper. The Michaelis-
Menten equation can be converted to a straight-line equation by taking the
reciprocals of each side, as shown in equation 14-8.
(14-8)
This treatment is called a double-reciprocal or Lineweaver-Burk plot. A
Lineweaver-Burk plot of the data in Figure 14-10 is shown in Figure 14-1 I.