Page 373 - Excel for Scientists and Engineers: Numerical Methods
P. 373
350 EXCEL: NUMERICAL METHODS
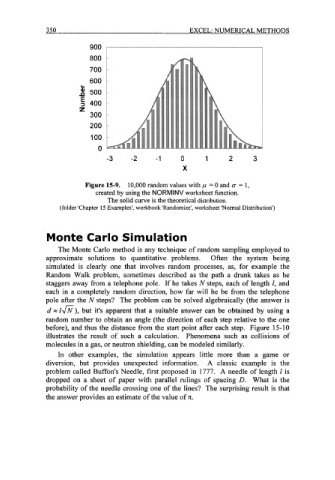
Figure 15-9. 10,000 random values with ,LI = 0 and cr = 1,
created by using the NORMINV worksheet function.
The solid curve is the theoretical distribution.
(folder 'Chapter 15 Examples', workbook 'Randomize', worksheet 'Normal Distribution')
Monte Carlo Simulation
The Monte Carlo method is any technique of random sampling employed to
approximate solutions to quantitative problems. Often the system being
simulated is clearly one that involves random processes, as, for example the
Random Walk problem, sometimes described as the path a drunk takes as he
staggers away from a telephone pole. If he takes N steps, each of length I, and
each in a completely random direction, how far will he be from the telephone
pole after the N steps? The problem can be solved algebraically (the answer is
d = lfi), but it's apparent that a suitable answer can be obtained by using a
random number to obtain an angle (the direction of each step relative to the one
before), and thus the distance from the start point after each step. Figure 15-10
illustrates the result of such a calculation. Phenomena such as collisions of
molecules in a gas, or neutron shielding, can be modeled similarly.
In other examples, the simulation appears little more than a game or
diversion, but provides unexpected information. A classic example is the
problem called Buffon's Needle, first proposed in 1777. A needle of length 1 is
dropped on a sheet of paper with parallel rulings of spacing D. What is the
probability of the needle crossing one of the lines? The surprising result is that
the answer provides an estimate of the value of 7c.