Page 200 - Facility Piping Systems Handbook for Industrial, Commercial, and Healthcare Facilities
P. 200
WATER TREATMENT AND PURIFICATION
4.36 CHAPTER FOUR
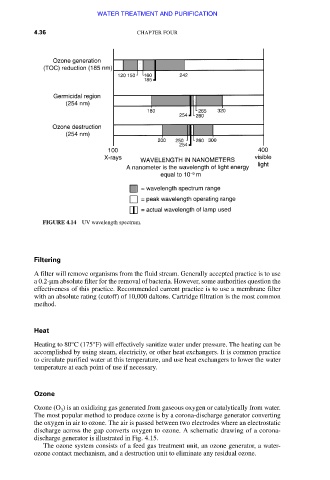
FIGURE 4.14 UV wavelength spectrum.
Filtering
A filter will remove organisms from the fluid stream. Generally accepted practice is to use
a 0.2-μm absolute filter for the removal of bacteria. However, some authorities question the
effectiveness of this practice. Recommended current practice is to use a membrane filter
with an absolute rating (cutoff) of 10,000 daltons. Cartridge filtration is the most common
method.
Heat
Heating to 80°C (175°F) will effectively sanitize water under pressure. The heating can be
accomplished by using steam, electricity, or other heat exchangers. It is common practice
to circulate purified water at this temperature, and use heat exchangers to lower the water
temperature at each point of use if necessary.
Ozone
Ozone (O ) is an oxidizing gas generated from gaseous oxygen or catalytically from water.
3
The most popular method to produce ozone is by a corona-discharge generator converting
the oxygen in air to ozone. The air is passed between two electrodes where an electrostatic
discharge across the gap converts oxygen to ozone. A schematic drawing of a corona-
discharge generator is illustrated in Fig. 4.15.
The ozone system consists of a feed gas treatment unit, an ozone generator, a water-
ozone contact mechanism, and a destruction unit to eliminate any residual ozone.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.accessengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.