Page 244 - Facility Piping Systems Handbook for Industrial, Commercial, and Healthcare Facilities
P. 244
HEAT TRANSFER, INSULATION, AND FREEZE PROTECTION
5.28 CHAPTER FIVE
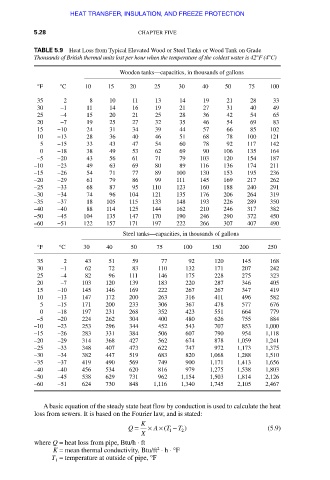
TABLE 5.9 Heat Loss from Typical Elevated Wood or Steel Tanks or Wood Tank on Grade
Thousands of British thermal units lost per hour when the temperature of the coldest water is 42°F (4°C)
Wooden tanks—capacities, in thousands of gallons
°F °C 10 15 20 25 30 40 50 75 100
35 2 8 10 11 13 14 19 21 28 33
30 −1 11 14 16 19 21 27 31 40 49
25 −4 15 20 21 25 28 36 42 54 65
20 −7 19 25 27 32 35 46 54 69 83
15 −10 24 31 34 39 44 57 66 85 102
10 −13 28 36 40 46 51 68 78 100 121
5 −15 33 43 47 54 60 78 92 117 142
0 −18 38 49 53 62 69 90 106 135 164
–5 −20 43 56 61 71 79 103 120 154 187
–10 −23 49 63 69 80 89 116 136 174 211
–15 −26 54 71 77 89 100 130 153 195 236
–20 −29 61 79 86 99 111 145 169 217 262
–25 −33 68 87 95 110 123 160 188 240 291
–30 −34 74 96 104 121 135 176 206 264 319
–35 −37 18 105 115 133 148 193 226 289 350
–40 −40 88 114 125 144 162 210 246 317 382
–50 −45 104 135 147 170 190 246 290 372 450
–60 −51 122 157 171 197 222 266 307 407 490
Steel tanks—capacities, in thousands of gallons
°F °C 30 40 50 75 100 150 200 250
35 2 43 51 59 77 92 120 145 168
30 –1 62 72 83 110 132 171 207 242
25 –4 82 96 111 146 175 228 275 323
20 –7 103 120 139 183 220 287 346 405
15 –10 145 146 169 222 267 267 347 419
10 –13 147 172 200 263 316 411 496 582
5 –15 171 200 233 306 367 478 577 676
0 –18 197 231 268 352 423 551 664 779
–5 –20 224 262 304 400 480 626 755 884
–10 –23 253 296 344 452 543 707 853 1,000
–15 –26 283 331 384 506 607 790 954 1,118
–20 –29 314 368 427 562 674 878 1,059 1,241
–25 –33 348 407 473 622 747 972 1,173 1,375
–30 –34 382 447 519 683 820 1,068 1,288 1,510
–35 –37 419 490 569 749 900 1,171 1,413 1,656
–40 –40 456 534 620 816 979 1,275 1,538 1,803
–50 –45 538 629 731 962 1,154 1,503 1,814 2,126
–60 –51 624 730 848 1,116 1,340 1,745 2,105 2,467
A basic equation of the steady state heat flow by conduction is used to calculate the heat
loss from sewers. It is based on the Fourier law, and is stated:
Q = K × A × ( T − T ) (5.9)
2
1
X
where Q = heat loss from pipe, Btu/h ⋅ ft
2
K = mean thermal conductivity, Btu/ft ⋅ h ⋅ °F
T = temperature at outside of pipe, °F
1
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.accessengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.