Page 255 - Facility Piping Systems Handbook for Industrial, Commercial, and Healthcare Facilities
P. 255
HEAT TRANSFER, INSULATION, AND FREEZE PROTECTION
HEAT TRANSFER, INSULATION, AND FREEZE PROTECTION 5.39
FIGURE 5.12 Average thermal conductivity for silt and clay soils.
structural engineer will have the soil tested for bearing strength. Part of this test is the
determination of moisture content. A copy of the engineer’s report should provide the
necessary information.
5. Volumetric latent heat of fusion L. This is a measure of the additional heat that must be
absorbed by the surrounding medium in order for the pore water to change its phase
state from water to ice. The more moisture a soil contains, the higher the L value. To find
L, multiply the latent heat of water (144) by the weight of the soil and by the moisture
content of the soil. This calculation is presented in graphic form in Fig. 5.14, where L
can be read directly.
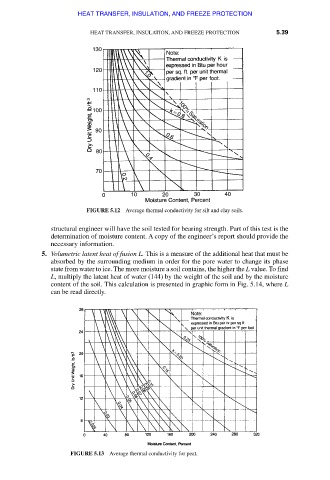
FIGURE 5.13 Average thermal conductivity for peat.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.accessengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2009 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.