Page 180 - Failure Analysis Case Studies II
P. 180
165
9
i
MULTIPLE ORIGIN FATIGUE
T TENSILE OVERLOAD
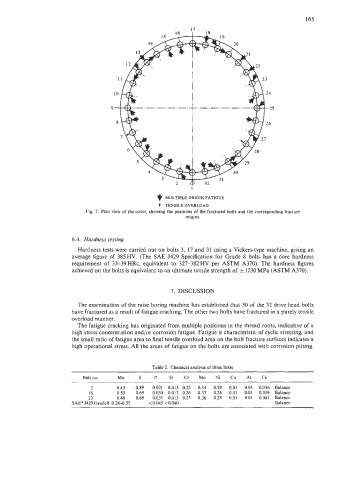
Fig. 7. Plan view of the cover, showing the positions of the fractured bolts and the corresponding fracture
origins.
6.4. Hardness testing
Hardness tests were carried out on bolts 3, 17 and 31 using a Vickers-type machine, giving an
average figure of 385HV. (The SAE 5429 Specification for Grade 8 bolts has a core hardness
requirement of 33-39 HRc, equivalent to 327-382 HV per ASTM A370). The hardness figures
achieved on the bolts is equivalent to an ultimate tensile strength of 1230 MPa (ASTM A370).
7. DISCUSSION
The examination of the raise boring machine has established that 30 of the 32 drive head bolts
have fractured as a result of fatigue cracking. The other two bolts have fractured in a purely tensile
overload manner.
The fatigue cracking has originated from multiple positions in the thread roots, indicative of a
high stress concentration and/or corrosion fatigue. Fatigue is characteristic of cyclic stressing, and
the small ratio of fatigue area to final tensile overload area on the bolt fracture surfaces indicates a
high operational stress. All the areas of fatigue on the bolts are associated with corrosion pitting.
Table 2. Chemical analysis of three bolts
Bok no. Mn S P Si Cr Mo Ni Cu AI Fe
2 0.43 0.89 0.021 0.013 0.22 0.34 0.29 0.01 0.01 0.036 Balance
16 0.50 0.69 0.030 0.013 0.26 0.37 0.26 0.01 0.01 0.039 Balance
23 0.48 0.69 0.031 0.013 0.25 0.36 0.25 0.01 0.01 0.041 Balance
SAE" 5429 Grade 8 0.28-0.55 <0.045 <0.040 Balance