Page 406 - Failure Analysis Case Studies II
P. 406
390
5
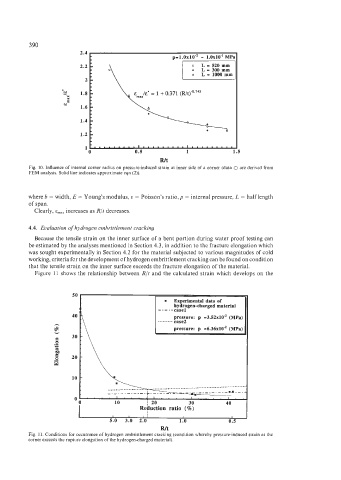
Fig. IO. Influence of internal comer radius on pressure-induced strain at inner side of a corner (data 0 are derived from
FEM analysis. Solid line indicates approximate eqn (2)).
where b = width, E = Young's modulus, u = Poisson's ratio, p = internal pressure, L = half length
of span.
Clearly, E,, increases as R/t decreases.
4.4. Evaluation of hydrogen embrittlement cracking
Because the tensile strain on the inner surface of a bent portion during water proof testing can
be estimated by the analyses mentioned in Section 4.3, in addition to the fracture elongation which
was sought experimentally in Section 4.2 for the material subjected to various magnitudes of cold
working, criteria for the development of hydrogen embrittlement cracking can be found on condition
that the tensile strain on the inner surface exceeds the fracture elongation of the material.
Figure 11 shows the relationship between R/t and the calculated strain which develops on the
50
40 re: p =3.52x102 (MPa)
30
.-
c)
m
M
C
0 20
Gi
10
0
Reauction ratio (%)
I I 1 - I I
5.0 3.0 2.0 1.0 0.5
R/t
Fig. 1 I. Conditions for occurrence of hydrogen embrittlement cracking (condition whereby pressure-induced strain at the
corner exceeds the rupture elongation of the hydrogen-charged material).