Page 404 - Failure Analysis Case Studies II
P. 404
388
Reduction ratio (9%)
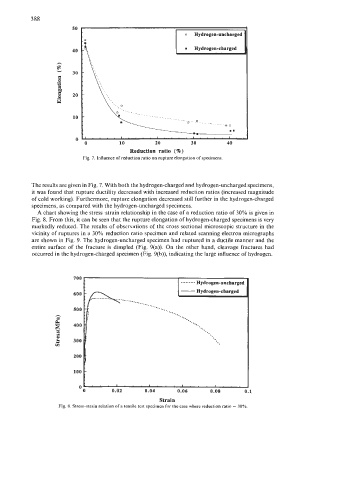
Fig. 7. Influence of reduction ratio on rupture elongation of specimens.
The results are given in Fig. 7. With both the hydrogen-charged and hydrogen-uncharged specimens,
it was found that rupture ductility decreased with increased reduction ratios (increased magnitude
of cold working). Furthermore, rupture elongation decreased still further in the hydrogen-charged
specimens, as compared with the hydrogen-uncharged specimens.
A chart showing the stress-strain relationship in the case of a reduction ratio of 30% is given in
Fig. 8. From this, it can be seen that the rupture elongation of hydrogen-charged specimens is very
markedly reduced. The results of obscrvations of thc cross scctional microscopic structure in the
vicinity of ruptures in a 30% reduction ratio specimen and related scanning electron micrographs
are shown in Fig. 9. The hydrogen-uncharged specimen had ruptured in a ductile manner and the
entire surface of the fracture is dimpled (Fig. 9(a)). On the other hand, cleavage fractures had
occurred in the hydrogen-charged specimen (Fig. 9(b)), indicating the large influence of hydrogen.
700
..- ...... Hydrogen-uncharged
- Hydrogen-charged
---..._._ -...
.-.
.--..
...
---..
....
-*._
*. .. .
1
Strain
Fig. 8. Stress-strain relation of a tensile test specimen for the case where reduction ratio = 30%.