Page 234 - Fair, Geyer, and Okun's Water and wastewater engineering : water supply and wastewater removal
P. 234
JWCL344_ch06_194-229.qxd 8/11/10 5:22 PM Page 195
6.1 Distribution Systems 195
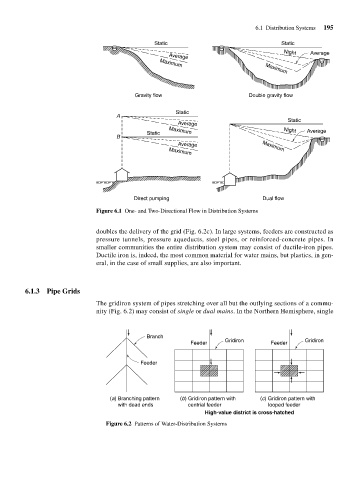
Static Static
Night Average
Average Maximum
Maximum
Gravity flow Double gravity flow
Static
A
Static
Average
Maximum Night Average
Static
B
Average Maximum
Maximum
Direct pumping Dual flow
Figure 6.1 One- and Two-Directional Flow in Distribution Systems
doubles the delivery of the grid (Fig. 6.2c). In large systems, feeders are constructed as
pressure tunnels, pressure aqueducts, steel pipes, or reinforced-concrete pipes. In
smaller communities the entire distribution system may consist of ductile-iron pipes.
Ductile iron is, indeed, the most common material for water mains, but plastics, in gen-
eral, in the case of small supplies, are also important.
6.1.3 Pipe Grids
The gridiron system of pipes stretching over all but the outlying sections of a commu-
nity (Fig. 6.2) may consist of single or dual mains. In the Northern Hemisphere, single
Branch
Feeder Gridiron Feeder Gridiron
Feeder
(a) Branching pattern (b) Gridiron pattern with (c) Gridiron pattern with
with dead ends centrial feeder looped feeder
High-value district is cross-hatched
Figure 6.2 Patterns of Water-Distribution Systems