Page 231 - Fair, Geyer, and Okun's Water and wastewater engineering : water supply and wastewater removal
P. 231
JWCL344_ch05_154-193.qxd 8/2/10 9:44 PM Page 192
192 Chapter 5 Water Hydraulics, Transmission, and Appurtenances
The measured residual pressures are as follows: The head delivered by the pumps to the water is 100 ft. The
Point B 300 kPa value of C for all pipes is 100. Assume the following elevations:
Point C 500 kPa A 900.00 ft
The known flows are as follows: B 9l5.00 ft
C 910.00 ft
Pipe BD 30 L/s
Pipe BE 75 L/s (a) Determine the required diameter of main PA, if the
pressure at point A is not allowed to drop below 52 psi.
C for all pipes 100.
(b) Determine the required diameter of pipe BC, if the
(a) Calculate the flow in line BC. maximum allowed head loss in the network ABC is
(b) Find the residual pressure at point D. 3 ft/1,000 ft.
(c) Compute the maximum water level in reservoir E. (c) Calculate the actual residual pressures at points A, B,
(d) Determine the required diameter for pipe AB.
and C.
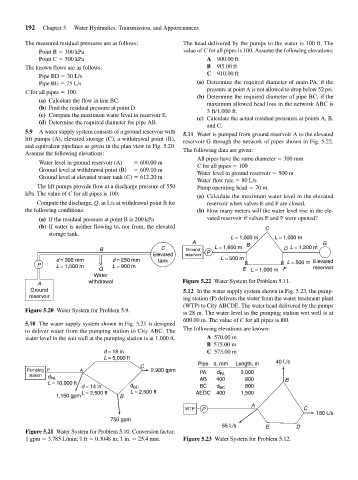
5.9 A water supply system consists of a ground reservoir with 5.11 Water is pumped from ground reservoir A to the elevated
lift pumps (A), elevated storage (C), a withdrawal point (B), reservoir G through the network of pipes shown in Fig. 5.22.
and equivalent pipelines as given in the plan view in Fig. 5.20.
Assume the following elevations: The following data are given:
All pipes have the same diameter 300 mm
Water level in ground reservoir (A) 600.00 m C for all pipes 100
Ground level at withdrawal point (B) 609.10 m Water level in ground reservoir 500 m
Ground level at elevated water tank (C) 612.20 m
Water flow rate 80 L/s
The lift pumps provide flow at a discharge pressure of 550 Pump operating head 70 m.
kPa. The value of C for all pipes is 100.
(a) Calculate the maximum water level in the elevated
Compute the discharge, Q, in L/s at withdrawal point B for reservoir when valves E and F are closed.
the following conditions: (b) How many meters will the water level rise in the ele-
(a) If the residual pressure at point B is 200 kPa vated reservoir if valves E and F were opened?
(b) If water is neither flowing to, nor from, the elevated C
storage tank.
L = 1,000 m L = 1,000 m
A B G
B C Ground L = 1,600 m D L = 1,200 m
Elevated reservoir P
d = 300 mm d = 250 mm tank L = 500 m L = 500 m Elevated
P L = 1,500 m L = 900 m
Q E L = 1,000 m F reservoir
Water
A withdrawal Figure 5.22 Water System for Problem 5.11.
Ground 5.12 In the water supply system shown in Fig. 5.23, the pump-
reservoir ing station (P) delivers the water from the water treatment plant
(WTP) to City ABCDE. The water head delivered by the pumps
Figure 5.20 Water System for Problem 5.9. is 28 m. The water level in the pumping station wet well is at
600.00 m. The value of C for all pipes is l00.
5.10 The water supply system shown in Fig. 5.21 is designed
to deliver water from the pumping station to City ABC. The The following elevations are known:
water level in the wet well at the pumping station is at 1,000 ft. A 570.00 m
B 575.00 m
d = 18 in C 573.00 m
L = 5,000 ft
Pipe d, mm Length, m 40 L/s
C
Pumping P A 2,900 gpm PA 3,000
station d PA
d PA AB 400 800 B
L = 10,000 ft
d = 14 in d BC BC d BC 800
L = 2,500 ft L = 2,500 ft AEDC 400 1,500
1,150 gpm B
A
WTP P C
180 L/s
750 gpm
55 L/s E D
Figure 5.21 Water System for Problem 5.10. Conversion factor:
1 gpm 3.785 L/min; 1 ft 0.3048 m; 1 in. 25.4 mm. Figure 5.23 Water System for Problem 5.12.