Page 236 - Fair, Geyer, and Okun's Water and wastewater engineering : water supply and wastewater removal
P. 236
JWCL344_ch06_194-229.qxd 8/2/10 9:51 PM Page 197
6.2 System Components 197
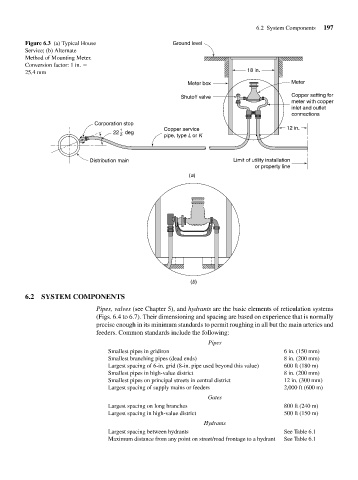
Figure 6.3 (a) Typical House Ground level
Service; (b) Alternate
Method of Mounting Meter.
Conversion factor: 1 in.
25.4 mm 18 in.
Meter box Meter
Shutoff valve Copper setting for
meter with copper
inlet and outlet
connections
Corporation stop
1 Copper service 12 in.
22 deg
2 pipe, type L or K
Distribution main Limit of utility installation
or property line
(a)
(b)
6.2 SYSTEM COMPONENTS
Pipes, valves (see Chapter 5), and hydrants are the basic elements of reticulation systems
(Figs. 6.4 to 6.7). Their dimensioning and spacing are based on experience that is normally
precise enough in its minimum standards to permit roughing in all but the main arteries and
feeders. Common standards include the following:
Pipes
Smallest pipes in gridiron 6 in. (150 mm)
Smallest branching pipes (dead ends) 8 in. (200 mm)
Largest spacing of 6-in. grid (8-in. pipe used beyond this value) 600 ft (180 m)
Smallest pipes in high-value district 8 in. (200 mm)
Smallest pipes on principal streets in central district 12 in. (300 mm)
Largest spacing of supply mains or feeders 2,000 ft (600 m)
Gates
Largest spacing on long branches 800 ft (240 m)
Largest spacing in high-value district 500 ft (150 m)
Hydrants
Largest spacing between hydrants See Table 6.1
Maximum distance from any point on street/road frontage to a hydrant See Table 6.1