Page 402 - Fiber Bragg Gratings
P. 402
8.5 The distributed feedback fiber laser 379
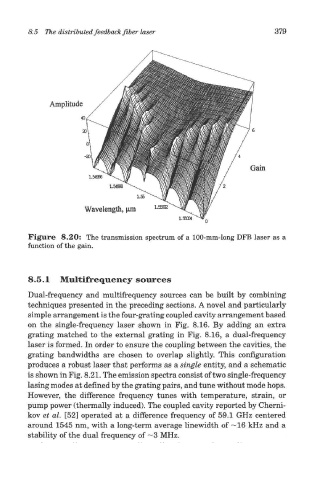
Figure 8.20: The transmission spectrum of a 100-mm-long DFB laser as a
function of the gain.
8.5.1 Multifrequency sources
Dual-frequency and multifrequency sources can be built by combining
techniques presented in the preceding sections. A novel and particularly
simple arrangement is the four-grating coupled cavity arrangement based
on the single-frequency laser shown in Fig. 8.16. By adding an extra
grating matched to the external grating in Fig. 8.16, a dual-frequency
laser is formed. In order to ensure the coupling between the cavities, the
grating bandwidths are chosen to overlap slightly. This configuration
produces a robust laser that performs as a single entity, and a schematic
is shown in Fig. 8.21. The emission spectra consist of two single-frequency
lasing modes at defined by the grating pairs, and tune without mode hops.
However, the difference frequency tunes with temperature, strain, or
pump power (thermally induced). The coupled cavity reported by Cherni-
kov et al. [52] operated at a difference frequency of 59.1 GHz centered
around 1545 nm, with a long-term average linewidth of ~16 kHz and a
stability of the dual frequency of ~3 MHz.