Page 404 - Fiber Bragg Gratings
P. 404
8.6 Bragg grating based pulsed sources 381
18,24,27,32]. We have also seen that the EDFGL is an excellent candidate
as a source [50]. There are several alternative methods of generating
short pulses in conjunction with gratings, for example, semiconductor
laser pulse compression in a chirped grating [91,92], using the dual-
frequency source and adiabatic soliton pulse compression [93] and linear
actively mode-locked fiber laser [94].
Pulse compression of gain-switched DFB and FP lasers [95] is possible
using a dispersive delay line, since the emitted pulse is chirped in time and
frequency. If the dispersion of the delay line is opposite to that of the pulse, it
maybe compressed. Chirped gratings (see Chapter 7) are ideal candidates,
since they are compact and the dispersion can be tailored for a particular
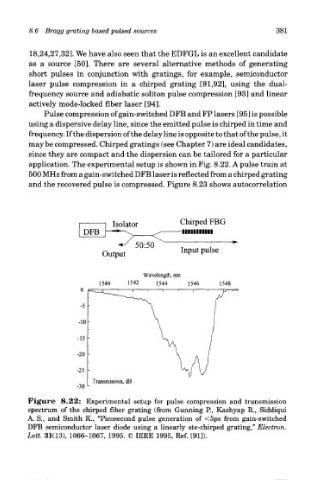
application. The experimental setup is shown in Fig. 8.22. A pulse train at
500 MHz from a gain-switched DFB laser is reflected from a chirped grating
and the recovered pulse is compressed. Figure 8.23 shows autocorrelation
Figure 8.22: Experimental setup for pulse compression and transmission
spectrum of the chirped fiber grating (from Gunning P., Kashyap R., Siddiqui
A. S., and Smith K., "Picosecond pulse generation of <5ps from gain-switched
DFB semiconductor laser diode using a linearly ste-chirped grating," Electron.
Lett. 31(13), 1066-1067, 1995. © IEEE 1995, Ref. [91]).