Page 443 - Fiber Bragg Gratings
P. 443
420 Chapter 9 Measurement and Characterization of Gratings
dispersion on the long-wavelength side of the band stop of apodized grat-
ings, useful for dense DWM systems. Note that the dispersion at the band
edge of the grating reaches several tens of picoseconds for the unapodized
grating and is much reduced in the apodized grating. Despite the apodiza-
tion, there is a curvature in the center of the band stop, which may be
useful to compensate for the chirp of a source [15].
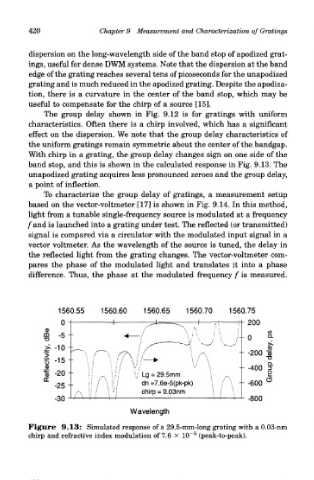
The group delay shown in Fig. 9.12 is for gratings with uniform
characteristics. Often there is a chirp involved, which has a significant
effect on the dispersion. We note that the group delay characteristics of
the uniform gratings remain symmetric about the center of the bandgap.
With chirp in a grating, the group delay changes sign on one side of the
band stop, and this is shown in the calculated response in Fig. 9.13. The
unapodized grating acquires less pronounced zeroes and the group delay,
a point of inflection.
To characterize the group delay of gratings, a measurement setup
based on the vector-voltmeter [17] is shown in Fig. 9.14. In this method,
light from a tunable single-frequency source is modulated at a frequency
/"and is launched into a grating under test. The reflected (or transmitted)
signal is compared via a circulator with the modulated input signal in a
vector voltmeter. As the wavelength of the source is tuned, the delay in
the reflected light from the grating changes. The vector-voltmeter com-
pares the phase of the modulated light and translates it into a phase
difference. Thus, the phase at the modulated frequency / is measured.
Figure 9.13: Simulated response of a 29.5-mm-long grating with a 0.03-nm
5
chirp and refractive index modulation of 7.6 x 1CT (peak-to-peak).