Page 311 - Fiber Fracture
P. 311
FRACTURE OF SYNTHETIC POLYMER FIBERS 293
activation theory, see Eqs. 1 and 2. At regular time intervals, the network of bonds is
relaxed towards mechanical equilibrium using fast convergence algorithms described in
Termonia et al. (1985).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Drawing of Unoriented Fiber
Efect of Molecular Weight
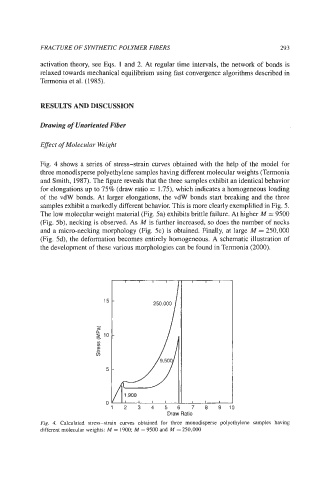
Fig. 4 shows a series of stress-strain curves obtained with the help of the model for
three monodisperse polyethylene samples having different molecular weights (Termonia
and Smith, 1987). The figure reveals that the three samples exhibit an identical behavior
for elongations up to 75% (draw ratio = 1.73, which indicates a homogeneous loading
of the vdW bonds. At larger elongations, the vdW bonds start breaking and the three
samples exhibit a markedly different behavior. This is more clearly exemplified in Fig. 5.
The low molecular weight material (Fig. 5a) exhibits brittle failure. At higher M = 9500
(Fig. 5b), necking is observed. As M is further increased, so does the number of necks
and a micro-necking morphology (Fig. 5c) is obtained. Finally, at large M = 250,000
(Fig. 5d), the deformation becomes entirely homogeneous. A schematic illustration of
the development of these various morphologies can be found in Termonia (2000).
15
m
g 10
u)
??
5
5
0
Draw Ratio
Fig. 4. Calculated stress-strain curves obtained for three monodisperse polyethylene samples having
different molecular weights: M = 1900; M = 9500 and M = 250,000