Page 385 - Fiber Fracture
P. 385
ATOMIC TRANSFORMATIONS 367
completely ductile region
0 moderately ductile region
brittle region A
zigzag
tubes = brittle region B
100 I
/
/
/
3
.- 50
c
zigzag
0 tubes
0 50
m index
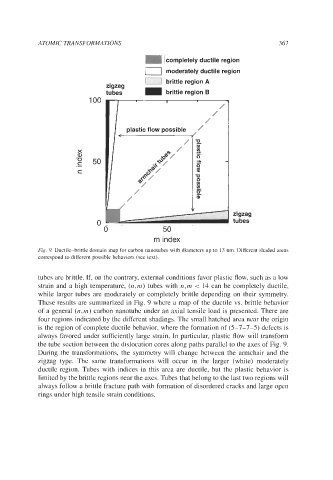
Fig. 9. Ductile-brittle domain map for carbon nanotubes with diameters up to 13 nm. Different shaded areas
correspond to different possible behaviors (see text).
tubes are brittle. If, on the contrary, external conditions favor plastic flow, such as a low
strain and a high temperature, (n,m) tubes with n,m < 14 can be completely ductile,
while larger tubes are moderately or completely brittle depending on their symmetry.
These results are summarized in Fig. 9 where a map of the ductile vs. brittle behavior
of a general (n,m) carbon nanotube under an axial tensile load is presented. There are
four regions indicated by the different shadings. The small hatched area near the origin
is the region of complete ductile behavior, where the formation of (5-7-7-5) defects is
always favored under sufficiently large strain. In particular, plastic flow will transform
the tube section between the dislocation cores along paths parallel to the axes of Fig. 9.
During the transformations, the symmetry will change between the armchair and the
zigzag type. The same transformations will occur in the larger (white) moderately
ductile region. Tubes with indices in this area are ductile, but the plastic behavior is
limited by the brittle regions near the axes. Tubes that belong to the last two regions will
always follow a brittle fracture path with formation of disordered cracks and large open
rings under high tensile strain conditions.