Page 94 - Finite Element Analysis with ANSYS Workbench
P. 94
5.2 Finite Element Method 85
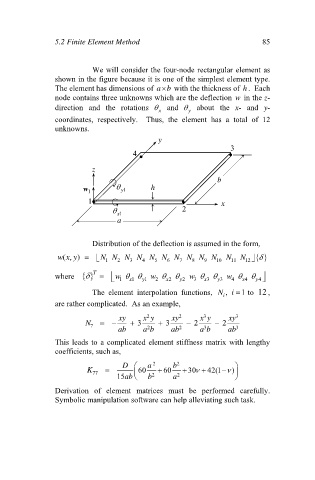
We will consider the four-node rectangular element as
shown in the figure because it is one of the simplest element type.
The element has dimensions of ab with the thickness of h. Each
node contains three unknowns which are the deflection w in the z-
direction and the rotations and about the x- and y-
y
x
coordinates, respectively. Thus, the element has a total of 12
unknowns.
y
3
4
z
b
w 1 1 y h
1 x
1 x 2
a
Distribution of the deflection is assumed in the form,
wx y NN N N N N N N N N 1 0 N 1 1 N 1 2
1
(, )
4
9
3
5
6
8
7
2
where T w 1 1 1 x w 2 y x 2 2 w 3 y 3 3 x w 4 y x 4 y 4
The element interpolation functions, N i 1 to 12 ,
,
i
are rather complicated. As an example,
2
xy x y xy 2 x y xy 3
3
N 3 3 2 2
7
3
ab a b ab 2 a b ab 3
2
This leads to a complicated element stiffness matrix with lengthy
coefficients, such as,
D a 2 b 2
K 60 60 30 42(1 )
15ab 77 b 2 a 2
Derivation of element matrices must be performed carefully.
Symbolic manipulation software can help alleviating such task.