Page 234 - Flexible Robotics in Medicine
P. 234
222 Chapter 9
bendable segments for guiding the hollow linkages to insert into the tracheal channel and
adjust the drill orientation, respectively. Two pulley mechanisms were used to stretch the
tendon wires for bending manipulation of the bendable joints.
9.3 Experimental procedure and results
9.3.1 Experimental setup
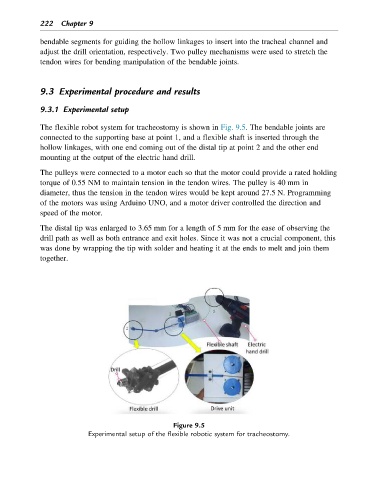
The flexible robot system for tracheostomy is shown in Fig. 9.5. The bendable joints are
connected to the supporting base at point 1, and a flexible shaft is inserted through the
hollow linkages, with one end coming out of the distal tip at point 2 and the other end
mounting at the output of the electric hand drill.
The pulleys were connected to a motor each so that the motor could provide a rated holding
torque of 0.55 NM to maintain tension in the tendon wires. The pulley is 40 mm in
diameter, thus the tension in the tendon wires would be kept around 27.5 N. Programming
of the motors was using Arduino UNO, and a motor driver controlled the direction and
speed of the motor.
The distal tip was enlarged to 3.65 mm for a length of 5 mm for the ease of observing the
drill path as well as both entrance and exit holes. Since it was not a crucial component, this
was done by wrapping the tip with solder and heating it at the ends to melt and join them
together.
Figure 9.5
Experimental setup of the flexible robotic system for tracheostomy.