Page 191 - Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics of Turbomachinery
P. 191
172 Fluid Mechanics, Thermodynamics of Turbomachinery
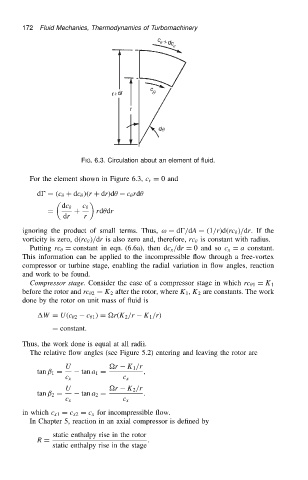
FIG. 6.3. Circulation about an element of fluid.
For the element shown in Figure 6.3, c r D 0 and
d D .c C dc /.r C dr/d c rd
dc c
D C rd dr
dr r
ignoring the product of small terms. Thus, ω D d/dA D .1/r/d.rc //dr.Ifthe
vorticity is zero, d.rc //dr is also zero and, therefore, rc is constant with radius.
Putting rc D constant in eqn. (6.6a), then dc x /dr D 0 and so c x D a constant.
This information can be applied to the incompressible flow through a free-vortex
compressor or turbine stage, enabling the radial variation in flow angles, reaction
and work to be found.
Compressor stage. Consider the case of a compressor stage in which rc 1 D K 1
before the rotor and rc 2 D K 2 after the rotor, where K 1 , K 2 are constants. The work
done by the rotor on unit mass of fluid is
c 1 / D r.K 2 /r K 1 /r/
W D U.c 2
D constant.
Thus, the work done is equal at all radii.
The relative flow angles (see Figure 5.2) entering and leaving the rotor are
U r K 1 /r
tan ˇ 1 D tan a 1 D ,
c x c x
U r K 2 /r
tan ˇ 2 D tan a 2 D .
c x c x
in which c x1 D c x2 D c x for incompressible flow.
In Chapter 5, reaction in an axial compressor is defined by
static enthalpy rise in the rotor
R D .
static enthalpy rise in the stage