Page 297 - Fluid Mechanics and Thermodynamics of Turbomachinery
P. 297
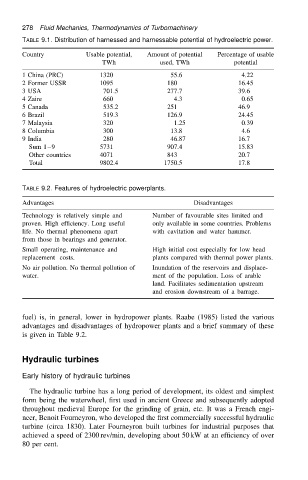
278 Fluid Mechanics, Thermodynamics of Turbomachinery
TABLE 9.1. Distribution of harnessed and harnessable potential of hydroelectric power.
Country Usable potential, Amount of potential Percentage of usable
TWh used, TWh potential
1 China (PRC) 1320 55.6 4.22
2 Former USSR 1095 180 16.45
3 USA 701.5 277.7 39.6
4 Zaire 660 4.3 0.65
5 Canada 535.2 251 46.9
6 Brazil 519.3 126.9 24.45
7 Malaysia 320 1.25 0.39
8 Columbia 300 13.8 4.6
9 India 280 46.87 16.7
Sum 1 9 5731 907.4 15.83
Other countries 4071 843 20.7
Total 9802.4 1750.5 17.8
TABLE 9.2. Features of hydroelectric powerplants.
Advantages Disadvantages
Technology is relatively simple and Number of favourable sites limited and
proven. High efficiency. Long useful only available in some countries. Problems
life. No thermal phenomena apart with cavitation and water hammer.
from those in bearings and generator.
Small operating, maintenance and High initial cost especially for low head
replacement costs. plants compared with thermal power plants.
No air pollution. No thermal pollution of Inundation of the reservoirs and displace-
water. ment of the population. Loss of arable
land. Facilitates sedimentation upstream
and erosion downstream of a barrage.
fuel) is, in general, lower in hydropower plants. Raabe (1985) listed the various
advantages and disadvantages of hydropower plants and a brief summary of these
is given in Table 9.2.
Hydraulic turbines
Early history of hydraulic turbines
The hydraulic turbine has a long period of development, its oldest and simplest
form being the waterwheel, first used in ancient Greece and subsequently adopted
throughout medieval Europe for the grinding of grain, etc. It was a French engi-
neer, Benoit Fourneyron, who developed the first commercially successful hydraulic
turbine (circa 1830). Later Fourneyron built turbines for industrial purposes that
achieved a speed of 2300 rev/min, developing about 50 kW at an efficiency of over
80 per cent.