Page 40 - Fluid Power Engineering
P. 40
Hydraulic Oils and Theor etical Backgr ound 17
For Newtonian fluids, the coefficient of dynamic viscosity, μ, is inde-
pendent of du/dy. However, it changes with temperature and pressure.
Kinematic viscosity, ν, is defined as the ratio of the dynamic viscosity
to the density.
μ
ν = (2.3)
ρ
2
where ν= Kinematic viscosity, m /s
ρ= Oil density, kg/m 3
The kinematic viscosity, ν, is often expressed in stokes (St), where
2
2
−4
2
−6
1 St = 10 m /s, or in centistokes (cSt), where 1 cSt = 10 m /s = 1 mm /s.
The viscosity units may be given in Redwood or Saybolt seconds,
or in degrees Engler, according to the measuring method. These units
are no longer used, but conversion tables are available.
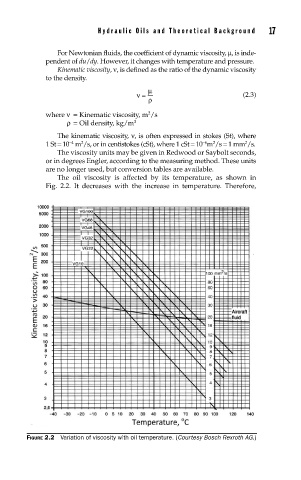
The oil viscosity is affected by its temperature, as shown in
Fig. 2.2. It decreases with the increase in temperature. Therefore,
FIGURE 2.2 Variation of viscosity with oil temperature. (Courtesy Bosch Rexroth AG.)