Page 230 - Fluid-Structure Interactions Slender Structure and Axial Flow (Volume 1)
P. 230
212 SLENDER STRUCTURES AND AXIAL FLOW
,
I I I I
0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6
a,
2s I I I I
o In air
air
o
In
0 In water
water
In
0
20 -
s- s-
15 -
10
0.2
0.4
0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6
0.6
0.0
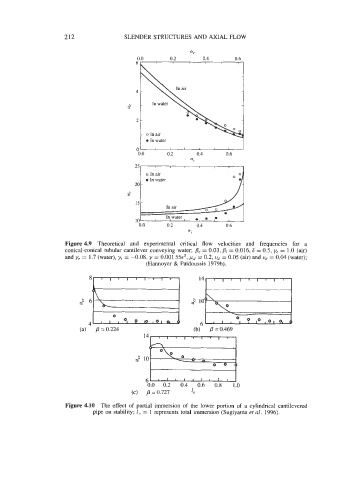
Figure 4.9 Theoretical and experimental critical flow velocities and frequencies for a
conical-conical tubular cantilever conveying water; Be = 0.03, Bi = 0.016,6 = 0.5, ye = 1.0 (air)
and ye = 1.7 (water), yj = -0.08, y = 0.001 55c3, wd = 0.2, ud = 0.05 (air) and vd = 0.04 (water);
(Hannoyer & PaTdoussis 1979b).
14 ,
0
6 '
(a) p = 0.224 (b) p =0.469
14,, , , , , I ,
6 -
0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
(c) /3 = 0.727 10
Figure 4.10 The effect of partial immersion of the lower portion of a cylindrical cantilevered
pipe on stability; 1, = 1 represents total immersion (Sugiyama ef al. 1996).