Page 126 - Fluid Catalytic Cracking Handbook
P. 126
102 Fluid Catalytic Cracking Handbook
0 1 2 3
Rare Earth, wt%
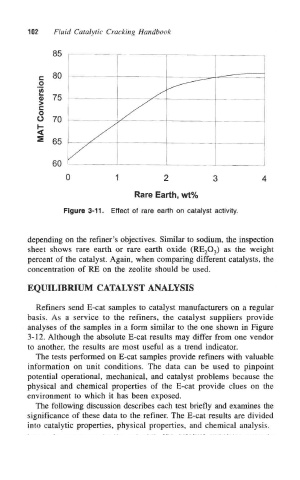
Figure 3-11. Effect of rare earth on catalyst activity.
depending on the refiner's objectives. Similar to sodium, the inspection
sheet shows rare earth or rare earth oxide (RE 2O 3) as the weight
percent of the catalyst. Again, when comparing different catalysts, the
concentration of RE on the zeolite should be used.
EQUILIBRIUM CATALYST ANALYSIS
Refiners send E-cat samples to catalyst manufacturers on a regular
basis. As a service to the refiners, the catalyst suppliers provide
analyses of the samples in a form similar to the one shown in Figure
3-12. Although the absolute E-cat results may differ from one vendor
to another, the results are most useful as a trend indicator.
The tests performed on E-cat samples provide refiners with valuable
information on unit conditions. The data can be used to pinpoint
potential operational, mechanical, and catalyst problems because the
physical and chemical properties of the E-cat provide clues on the
environment to which it has been exposed.
The following discussion describes each test briefly and examines the
significance of these data to the refiner. The E-cat results are divided
into catalytic properties, physical properties, and chemical analysis.