Page 131 - Fluid Catalytic Cracking Handbook
P. 131
106 Fluid Catalytic Cracking Handbook
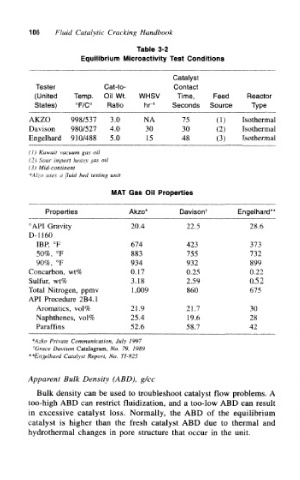
Table 3-2
Equilibrium Microactivity Test Conditions
Catalyst
Tester Cat-to- Contact
(United Temp. Oil Wt. WHSV Time, Feed Reactor
States) °F/C° Ratio hr 1 Seconds Source Type
AKZO 998/537 3.0 NA 75 (1) Isothermal
Davisoe 980/527 4.0 30 30 (2) Isothermal
Engelhard 910/488 5.0 15 48 (3) Isothermal
(}) Kuwait vacuum gas oil
(2) Sour import heavy gas oil
(3) Mid-continent
*Alzo uses a fluid bed testing unit
MAT Gas Oil Properties
Properties Akzo* Davison* Engelhard**
°API Gravity 20.4 22.5 28.6
D-1160
IBP, °F 674 423 373
50%, °F 883 755 732
90%, °F 934 932 899
Conearbon, wt% 0.17 0.25 0.22
Sulfur, wt% 3.18 2.59 0.52
Total Nitrogen, ppmv 1,009 860 675
API Procedure 2B4.1
Aromatics, vol% 21.9 21.7 30
Naphthenes, vol% 25.4 19.6 28
Paraffins 52.6 58.7 42
*Azko Private Communication, July 1997
f
Grace Davison Catalagram, No. 79, 1989
**Engelhard Catalyst Report, No. Tl-825
Apparent Bulk Density (ABD), g/cc
Bulk density can be used to troubleshoot catalyst flow problems. A
too-high ABD can restrict fluidization, and a too-low ABD can result
in excessive catalyst loss. Normally, the ABD of the equilibrium
catalyst is higher than the fresh catalyst ABD due to thermal and
hydrothermal changes in pore structure that occur in the unit.